CPG Schema¶
This document describes the kinds of nodes and edges in the CPG, along with the various attributes attached to them. It is generated from the MATE JSON schemata.
Nodes¶
LocalVariable¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to LocalVariable nodes:
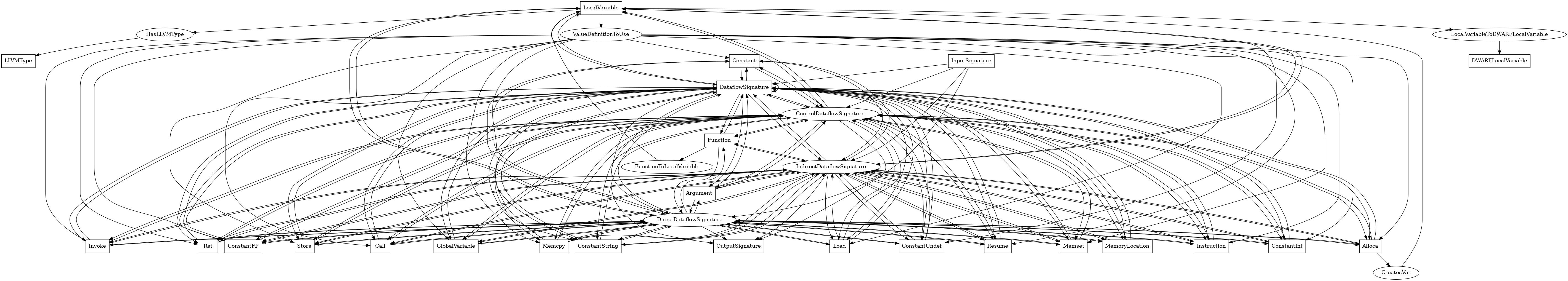
An LLVM-level stack-local variable
Attributes:
pretty_stringtype:
string
name: The source-level name of this local variabletype:
string
location: The variable’s location: #/definitions/locationnode_kind
DWARFLocalVariable¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to DWARFLocalVariable nodes:
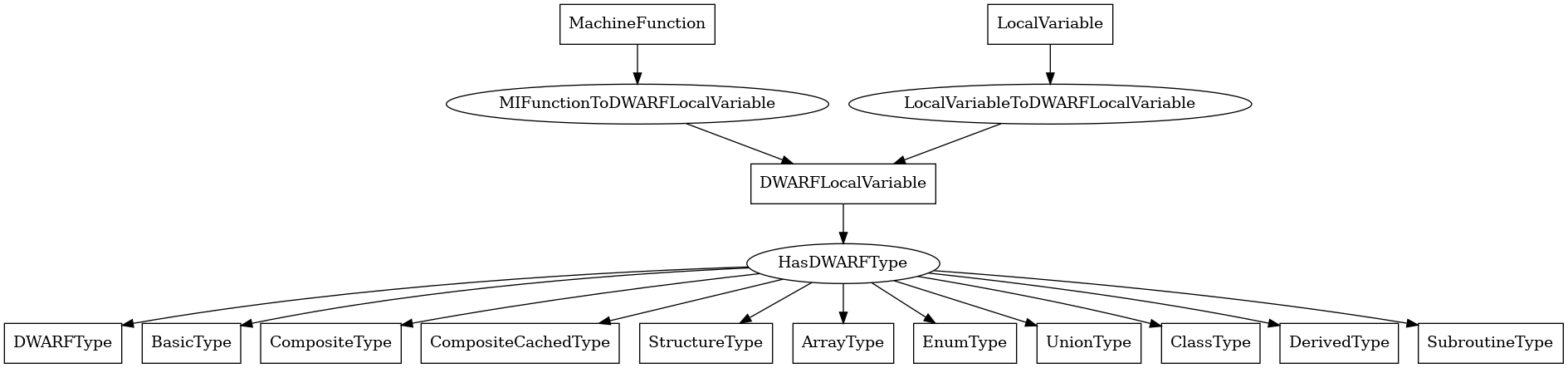
A DWARF-level stack-local variable
Attributes:
node_kindnametype:
string
kindargparametertype_id: A compressed representation of the function’s DWARF typetype:
string
dwarf_scope: The variable’s DWARF scope: #/definitions/dwarf_scopesource_location: The variable’s source location: #/definitions/source_locationsource_scope: The variable’s source scope: #/definitions/source_scopeartificial: Whether the variable is artificialtype:
boolean
dwarf_location: The memory location of this local variable, if not optimized away: #/definitions/dwarf_location
ASMGlobalVariable¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ASMGlobalVariable nodes:
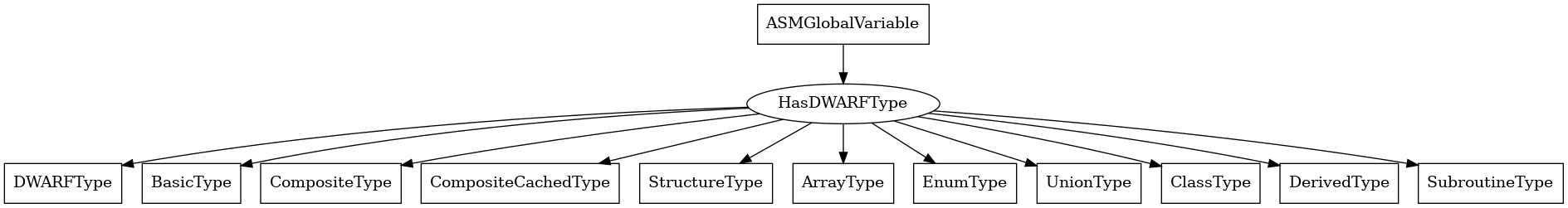
A program global variable at the binary level
Attributes:
node_kindpretty_stringtype:
string
thread_localtype:
boolean
definition_location: #/definitions/definition_locationdefinition: Indicates whether this visitation of the global variable is a definitiontype:
boolean
local_to_unit: Indicates whether or not this global variable is local to this translation unittype:
boolean
source_scope: #/definitions/source_scopetype_idtype:
string
name: The source-level name of this global variabletype:
string
dwarf_location: #/definitions/dwarf_locationvatype:
integer
Function¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Function nodes:
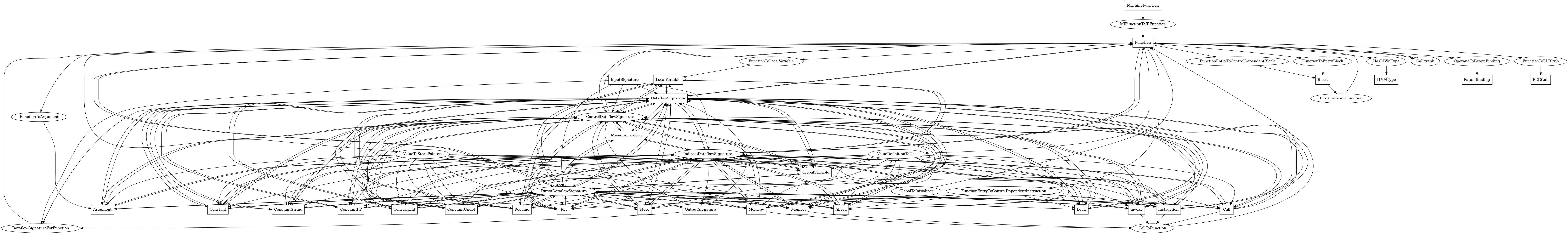
LLVM IR functions
Attributes:
node_kindname: The name of the LLVM function. For functions generated by compiling C code, this is often the same name that appears in the source, e.g. ‘@recv’ (at the LLVM level) corresponds to ‘recv’ (at the C level). However, compiled from other languages, the names will often be mangled. The source-level name will generally appear as a substring in the LLVM-level name.type:
string
demangled_name: The demangled name of the function.type:
string
is_declaration: True if this function has no definition.type:
boolean
alignmenttype:
integer
sectiontype:
string
location: #/definitions/locationpretty_stringtype:
string
Argument¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Argument nodes:
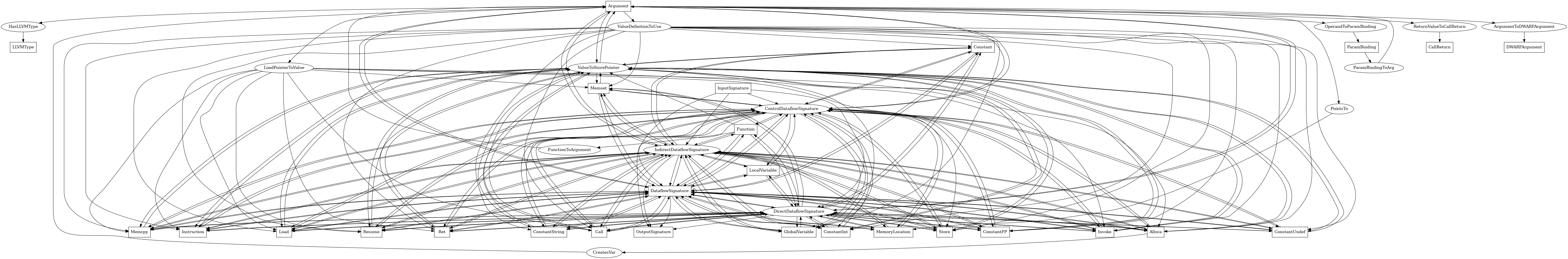
A formal parameter to an LLVM function
Attributes:
pretty_stringtype:
string
name: The source-level name of this formal parametertype:
string
node_kindlocation: #/definitions/locationmight_be_null: True when the pointer analysis determines the parameter could be a null pointertype:
boolean
argument_numbertype:
integer
DWARFArgument¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to DWARFArgument nodes:
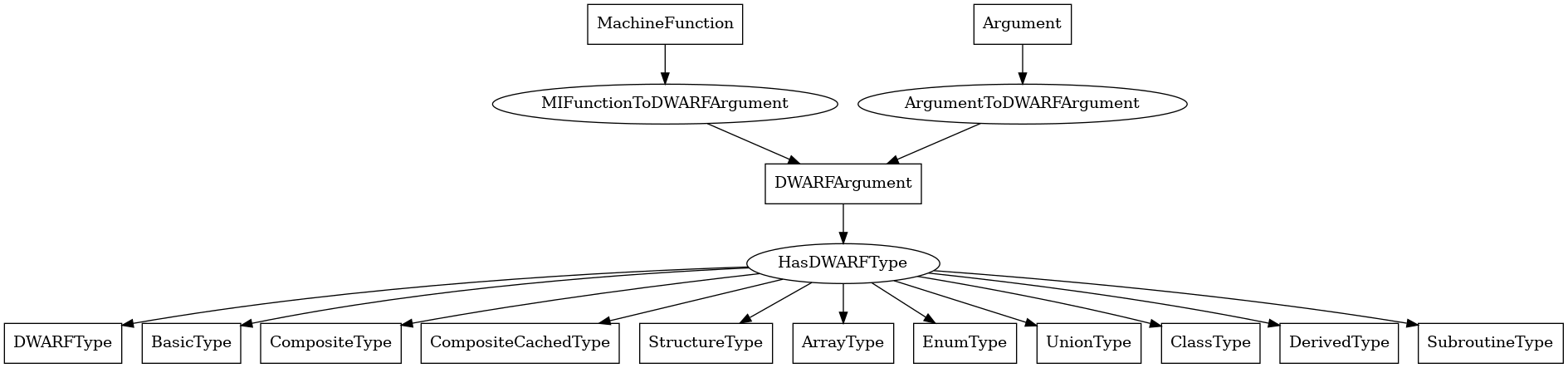
A DWARF-level formal parameter to a function
Attributes:
node_kindkindargtype:
integer
parametername: The source-level name of this formal parametertype:
string
dwarf_location: The memory location of this formal parameter, if not optimized away: #/definitions/dwarf_locationtype_idtype:
string
dwarf_scope: #/definitions/dwarf_scopesource_location: #/definitions/source_locationsource_scope: #/definitions/source_scopeartificialtype:
boolean
from_variadic_template: True if this parameter is from a variadic template expansion; does not exist otherwisetype:
boolean
original_name: The original name of this argument, with no variadic index suffixtype:
string
parameter_index: The index of this argument into the overall list of arguments to the enclosing functiontype:
integer
variadic_index: The index of this argument into all variadic arguments of this functiontype:
integer
template_index: The index of this argument into the variadic arguments of its group (i.e., those with the same name)type:
integer
Block¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Block nodes:
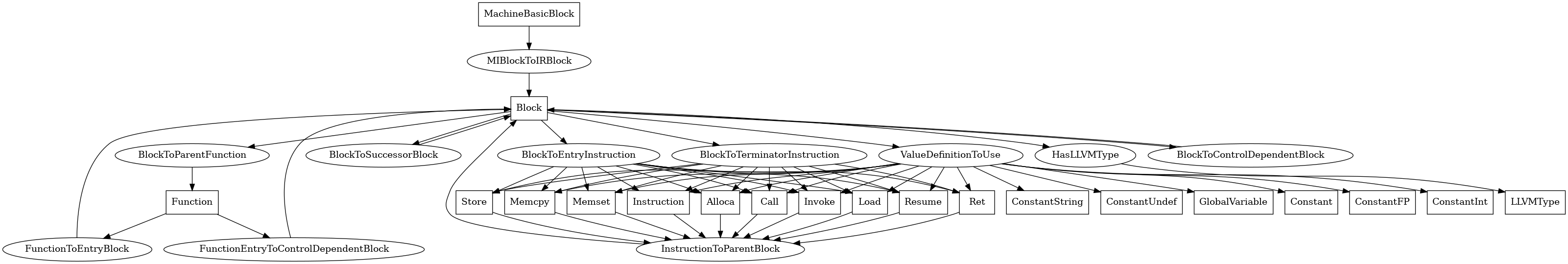
LLVM IR basic blocks
Attributes:
node_kindpretty_stringtype:
string
labeltype:
string
GlobalVariable¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to GlobalVariable nodes:
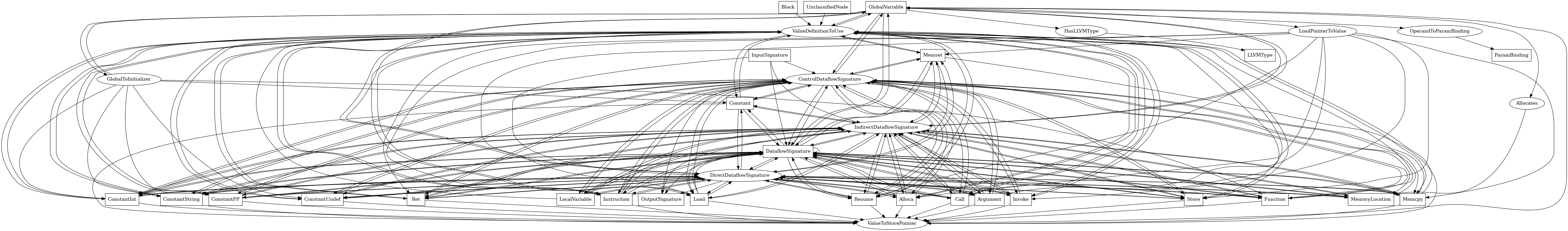
A program global variable at the LLVM level
Attributes:
node_kindis_constanttype:
boolean
is_declaration: True if this global variable has no definition.type:
boolean
has_initializertype:
boolean
nametype:
string
alignmenttype:
integer
sectiontype:
string
location: #/definitions/locationpretty_stringtype:
string
Instruction¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Instruction nodes:
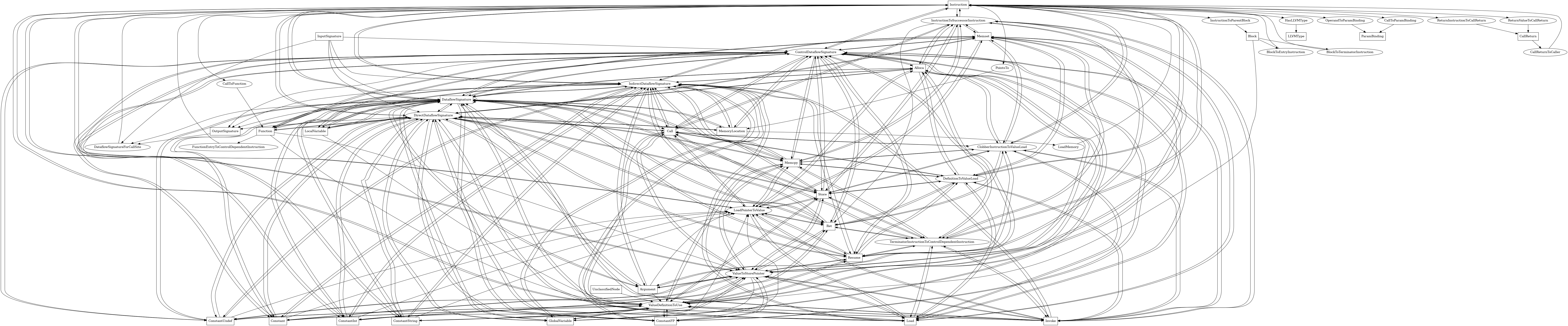
LLVM IR instructions
Attributes:
node_kind
Alloca¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Alloca nodes:
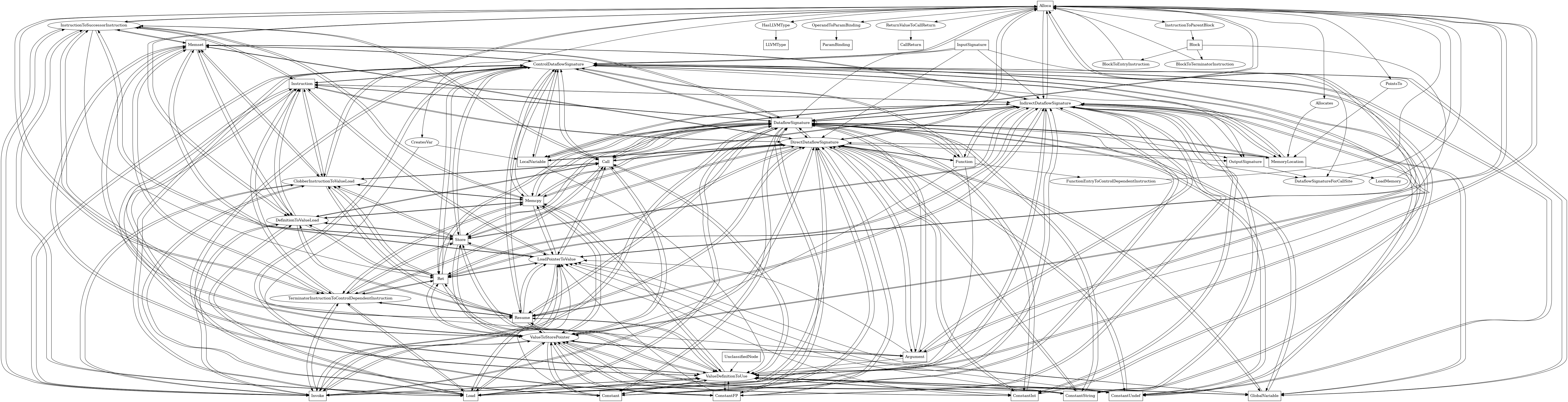
LLVM IR alloca instructions
Attributes:
node_kind
Call¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Call nodes:
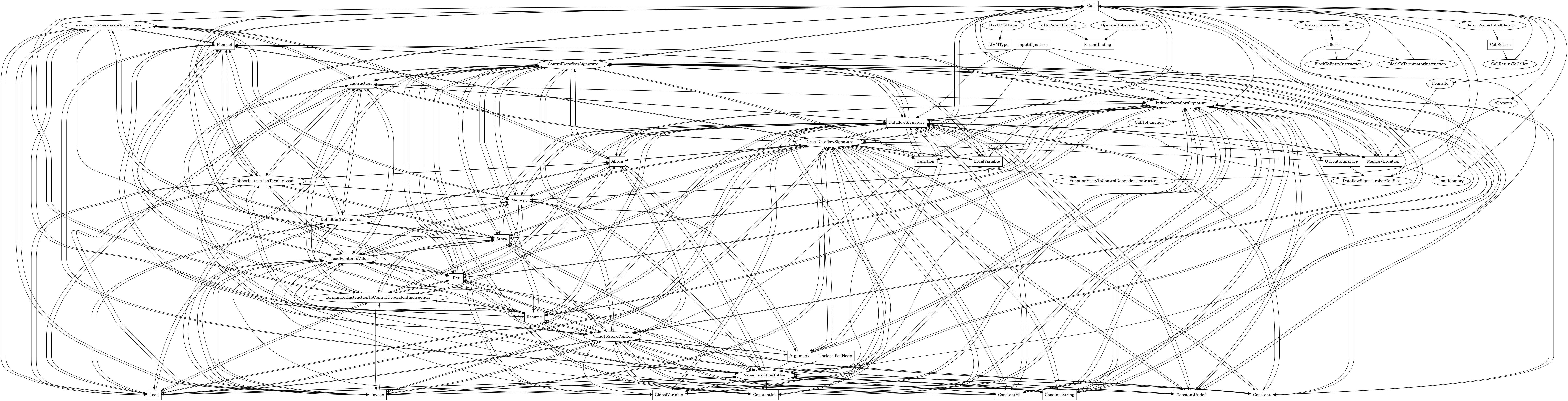
LLVM IR call instructions
Attributes:
node_kindis_directtype:
boolean
Invoke¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Invoke nodes:
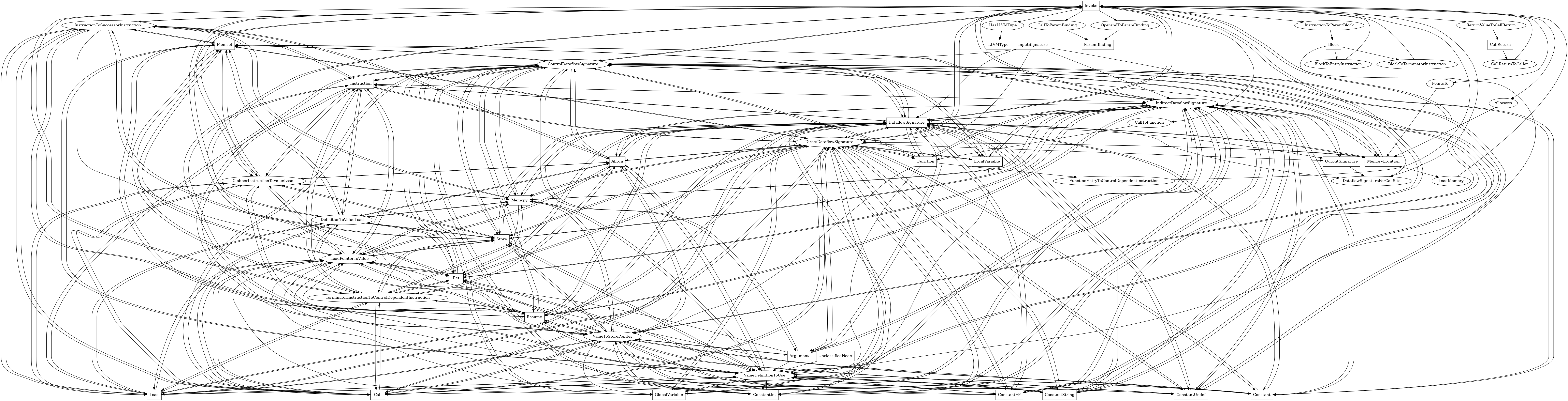
LLVM IR invoke instructions
Attributes:
node_kindis_directtype:
boolean
Memcpy¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Memcpy nodes:
LLVM IR memcpy intrinsics
Attributes:
node_kind
Memset¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Memset nodes:
LLVM IR memset intrinsics
Attributes:
node_kind
Load¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Load nodes:
LLVM IR load instructions
Attributes:
node_kind
Resume¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Resume nodes:
LLVM IR resume instructions
Attributes:
node_kind
Ret¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Ret nodes:
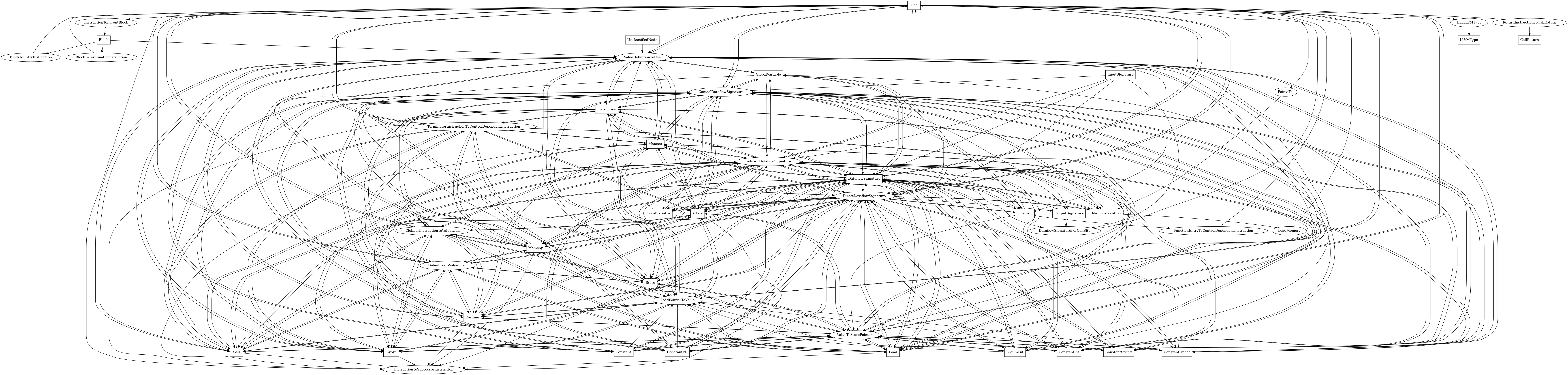
LLVM IR ret instructions
Attributes:
node_kind
Store¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Store nodes:
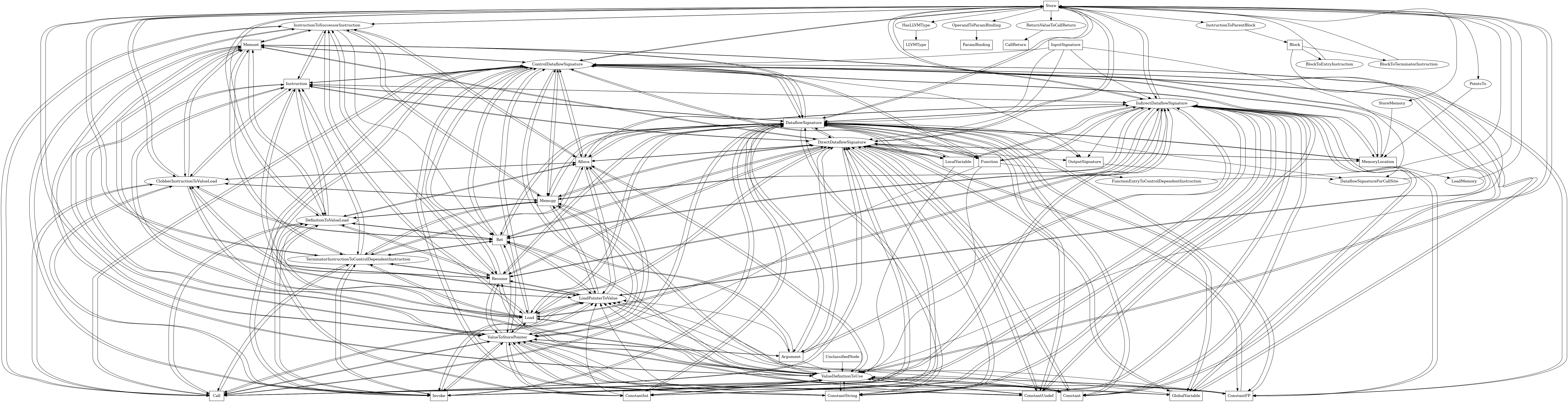
LLVM IR store instructions
Attributes:
node_kind
LLVMType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to LLVMType nodes:

A type in the LLVM type system. See https://llvm.org/docs/LangRef.html#type-system for details.
Attributes:
node_kindtype:
object
definition: #/definitions/llvm_typetype:
object
size_in_bits: The number of bits necessary to hold the specified type. The following table (taken from the LLVM source code, see “Legal” in the documentation) contrasts this field with other size-related fields.
/// Size examples:
///
/// Type SizeInBits StoreSizeInBits AllocSizeInBits[*]
/// ---- ---------- --------------- ---------------
/// i1 1 8 8
/// i8 8 8 8
/// i19 19 24 32
/// i32 32 32 32
/// i100 100 104 128
/// i128 128 128 128
/// Float 32 32 32
/// Double 64 64 64
/// X86_FP80 80 80 96
///
/// [*] The alloc size depends on the alignment, and thus on the target.
/// These values are for x86-32 linux.
- type: ``integer``
store_size_in_bits: the maximum number of bits that may be overwritten by storing the specified type; always a multiple of 8type:
integer
alloc_size_in_bits: the offset in bits between successive objects of the specified type, including alignment padding; always a multiple of 8type:
integer
abi_type_alignment: the minimum ABI-required alignment for this typetype:
integer
pretty_stringtype:
string
Constant¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Constant nodes:
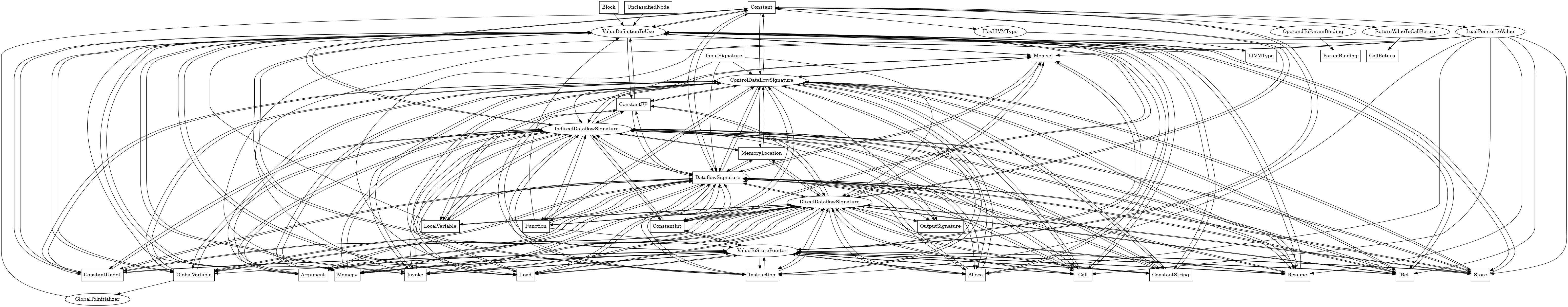
A constant value in the LLVM IR
Attributes:
node_kind
Variable¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Variable nodes:

A variable in the LLVM IR
Attributes:
node_kind
ConstantInt¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ConstantInt nodes:
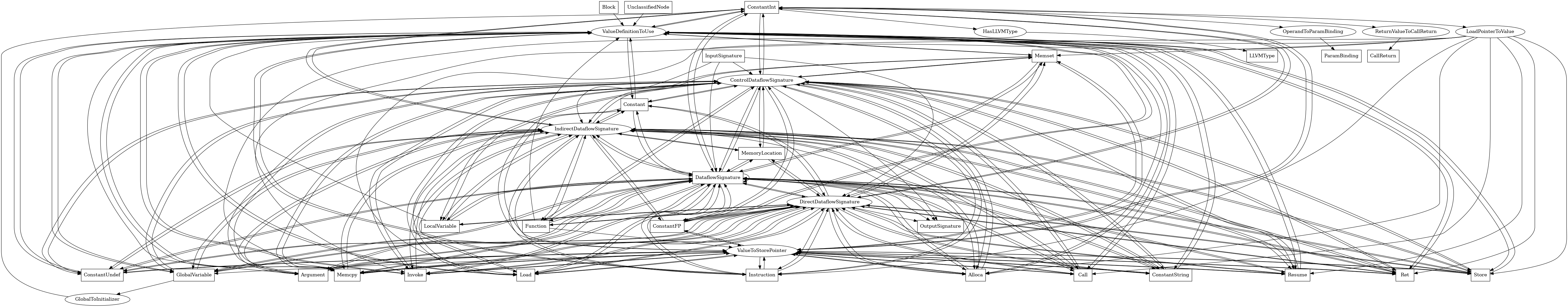
A constant int value in the LLVM IR
Attributes:
node_kindconstant_data_subclassconstant_int_value: The value of this integer constant.type:
integer
ConstantFP¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ConstantFP nodes:
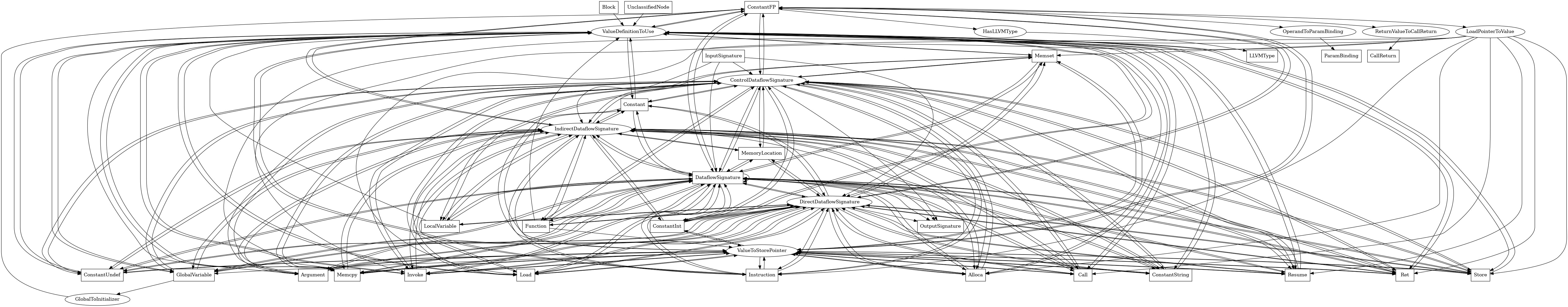
A constant floating point value in the LLVM IR
Attributes:
node_kindconstant_data_subclass
ConstantString¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ConstantString nodes:
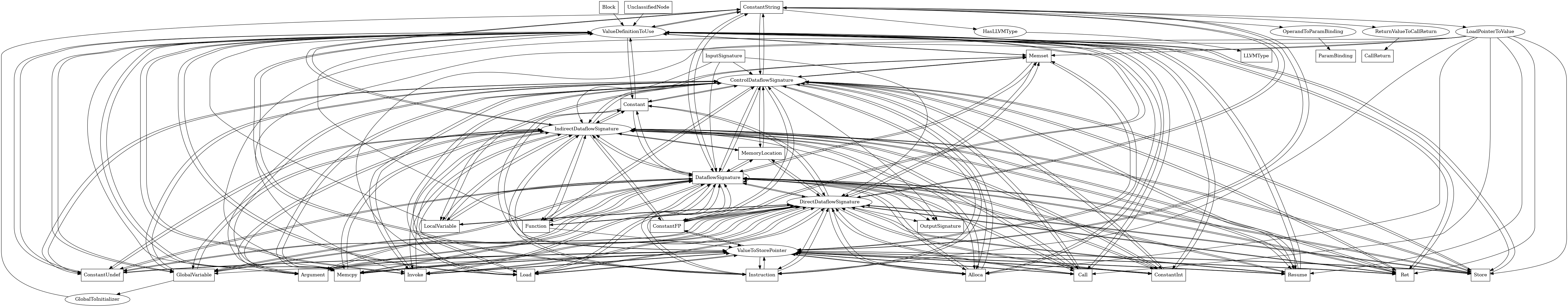
A constant string value in the LLVM IR
Attributes:
node_kindstring_valuetype:
string
ConstantUndef¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ConstantUndef nodes:
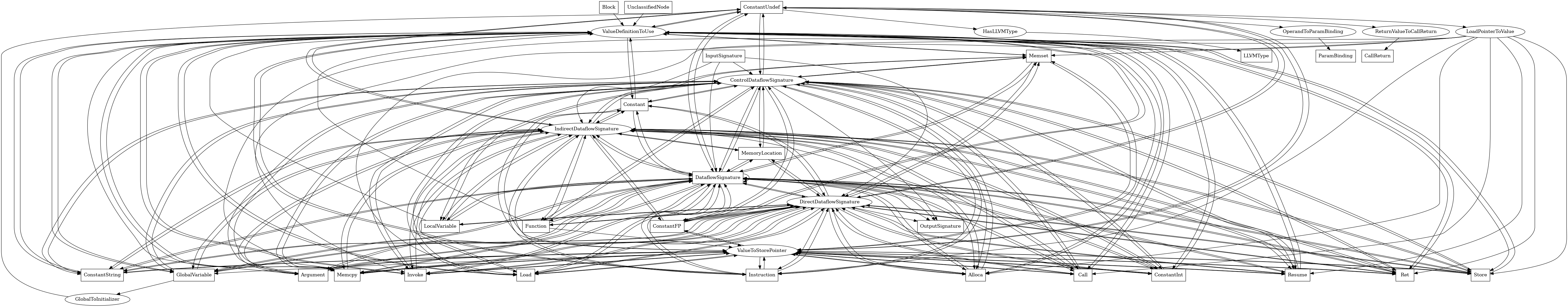
An undef value in the LLVM IR
Attributes:
node_kindconstant_data_subclass
UnclassifiedNode¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to UnclassifiedNode nodes:
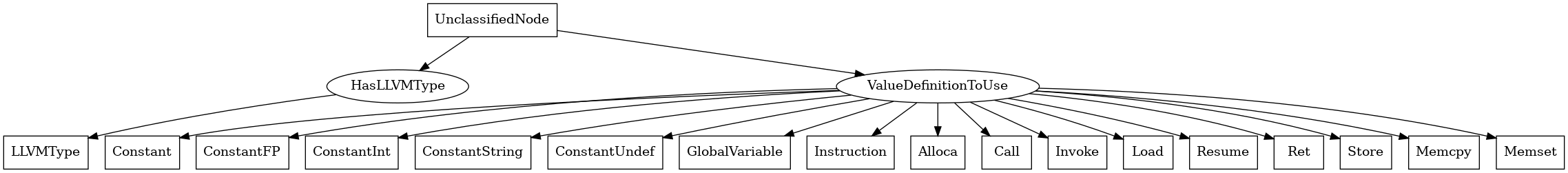
An as-of-yet underspecified node of the LLVM AST
Attributes:
node_kindpretty_stringtype:
string
MachineFunction¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to MachineFunction nodes:
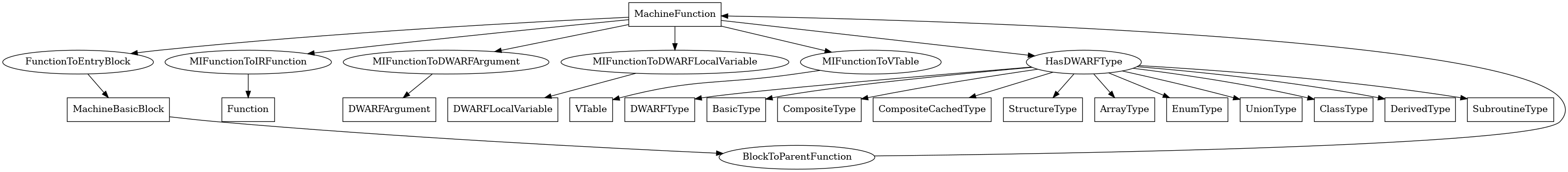
Named after the eponymous LLVM class, these nodes represent the LLVM middle-end’s concept of a function.
Attributes:
node_kindoffset: The offset into the binary itself where this function is located.type:
integer
va_start: The VA (Virtual Address) tells us where this function is located in the binary.type:
integer
va_end: The VA (Virtual Address) tells us the last VA where the function is located in the binary.type:
integer
prologues: Pairs of VA (Virtual Address) ranges where the function contains prologue code (e.g., stack setup)type:
array
epilogues: Pairs of VA (Virtual Address) ranges where the function contains epilogue code (e.g., stack teardown)type:
array
operand: TODO(lb)type:
string
name: The corresponding LLVM IR function’s nametype:
string
is_mangled: Whether or not this function’s name has been mangledtype:
boolean
demangled_name: The demangled function name, or the regular name if not mangledtype:
string
frame_info: Information about this function’s stack frametype:
object
type_id: A compressed representation of the function’s DWARF typetype:
string
pretty_string: A pretty representation of the functiontype:
string
source: A list of source entries for this functiontype:
array
symbols: The function’s binary symbolstype:
array
MachineBasicBlock¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to MachineBasicBlock nodes:
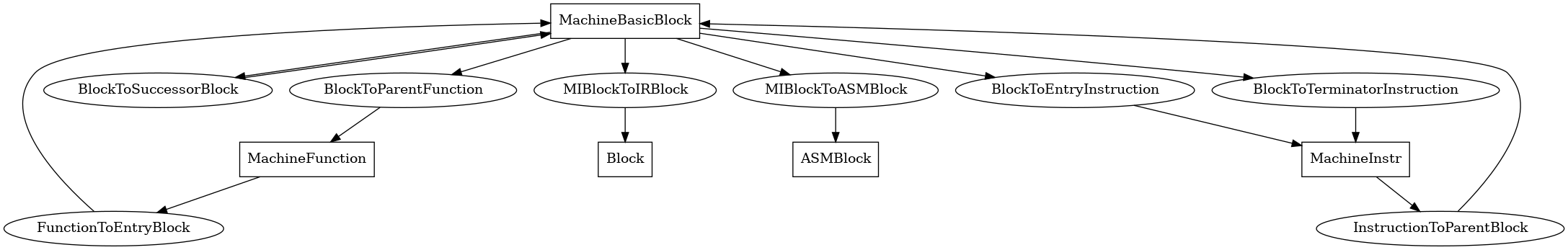
Named after the eponymous LLVM class, these nodes represent the LLVM middle-end’s concept of a basic block.
Attributes:
node_kindpretty_stringtype:
string
number: The numeric identifier for this basic blocktype:
integer
symbol: The machine-addressable symbol for this basic blocktype:
string
can_fallthrough: Whether or not this basic block can implicitly transfer control flow by falling through to the nexttype:
boolean
ends_in_return: Whether or not this basic block ends in a returntype:
boolean
is_epilogue_insertion_block: Whether or not this basic block will contain generated epilogue code (e.g., for stack cleanup)type:
boolean
is_prologue_insertion_block: Whether or not this basic block will contain generated prologue code (e.g., for stack setup)type:
boolean
address_taken: Whether or not this basic block is potentially a target of an indirect branchtype:
boolean
has_inline_asm: Whether or not this block contains inlined assembly statementstype:
boolean
preds: The array of predecessor blocks, identified by their symbolstype:
array
succs: The array of successor blocks, identified by their symbolstype:
array
instrs: The array of middle-end instructions in this blocktype:
array
MachineInstr¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to MachineInstr nodes:
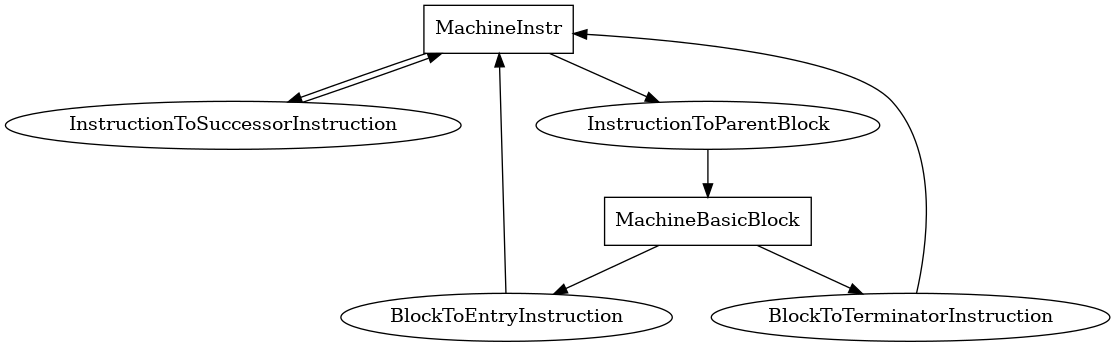
Named after the eponymous LLVM class, these nodes represent the LLVM middle-end’s concept of an instruction.
Attributes:
node_kindpretty_stringtype:
string
opcodetype:
integer
flagstype:
integer
ASMInst¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ASMInst nodes:
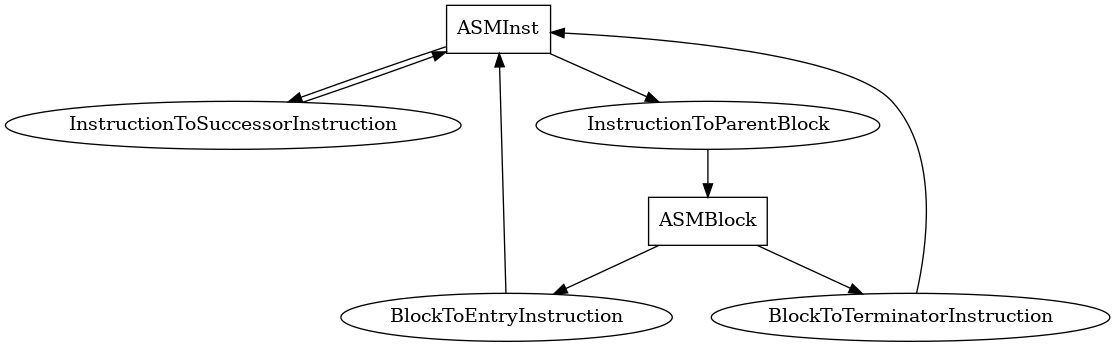
An x86_64 instruction in the binary, including layout and semantic information
Attributes:
node_kindpretty_stringtype:
string
vatype:
integer
size: The decoded size of this instruction, in bytestype:
integer
mnemonic: The assembly mnemonic for this instructiontype:
string
asm: The disassembled instruction, in Intel formattype:
string
used_registers: An array of register use information for this instructiontype:
array
used_memory: An array of memory use information for this instructiontype:
array
ASMBlock¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ASMBlock nodes:
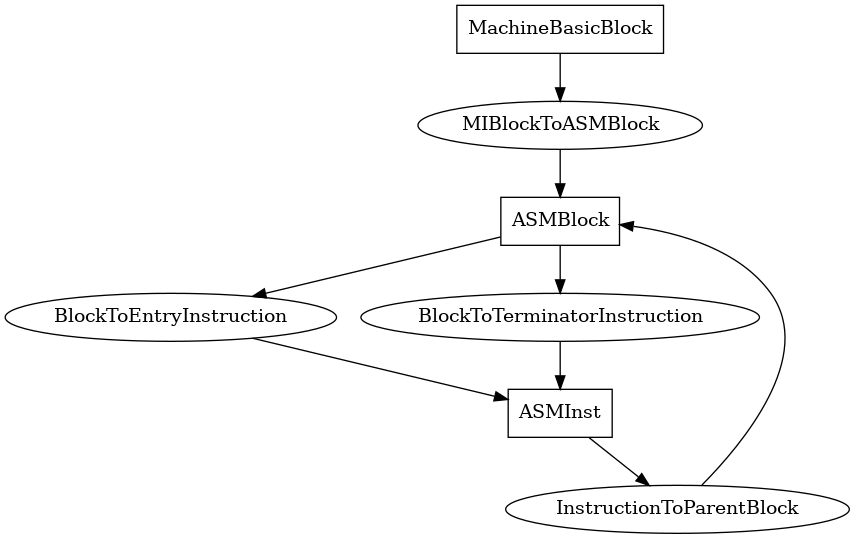
A basic block in the x86_64 binary
Attributes:
node_kindpretty_stringtype:
string
unpairedtype:
boolean
vatype:
integer
va_endtype:
integer
size: The size of this basic block, in bytestype:
integer
offsettype:
integer
func_offsettype:
integer
func_referencetype:
string
sourcetype:
array
filenametype:
string
ParamBinding¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ParamBinding nodes:
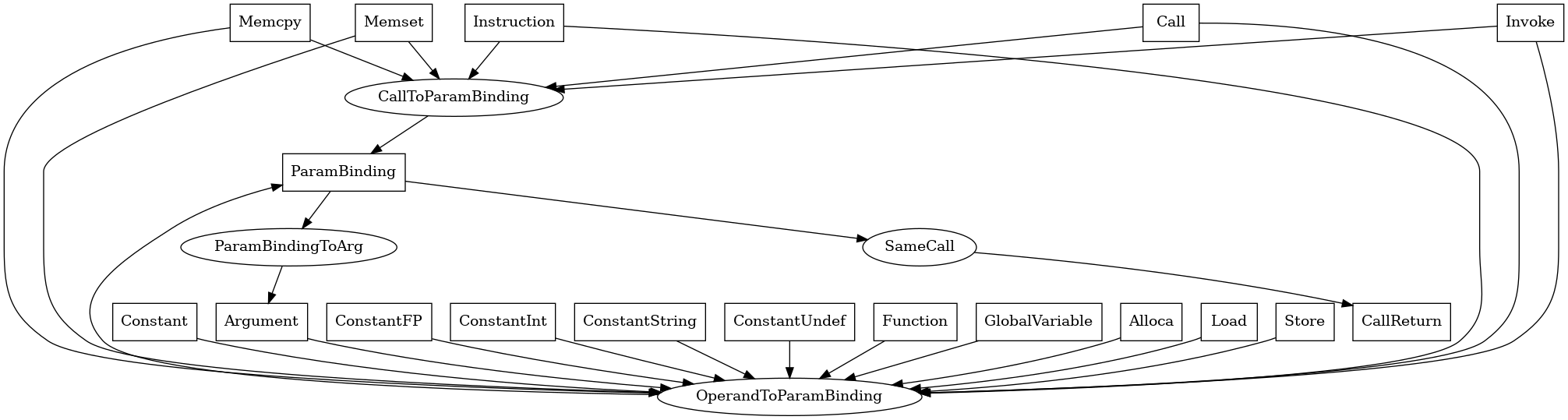
A node which connects argument values with formal parameters
Attributes:
node_kindarg_op_numbertype:
integer
CallReturn¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to CallReturn nodes:
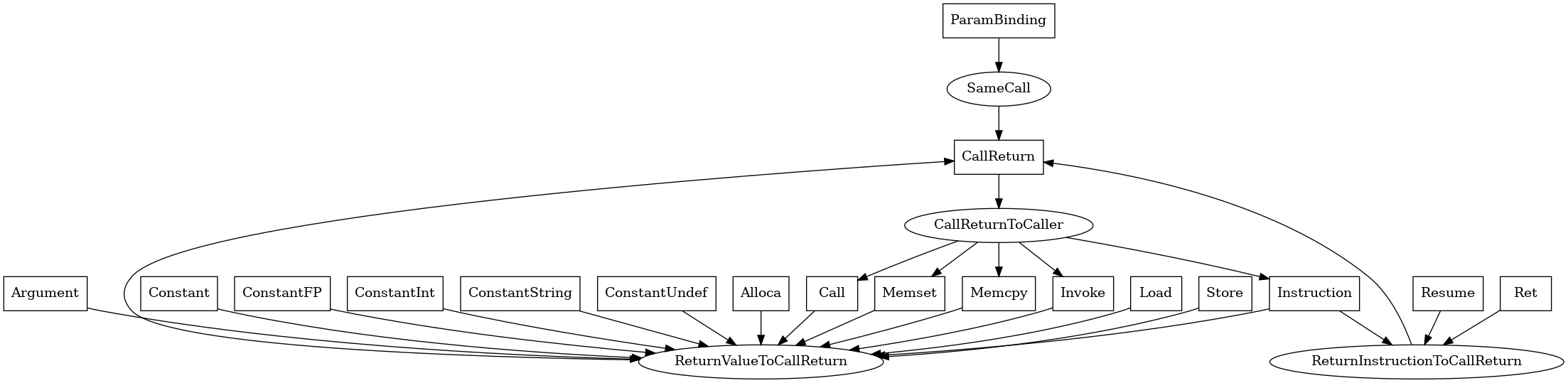
A node that connects a value used in a return statement to the corresponding call site.
Attributes:
node_kind
MemoryLocation¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to MemoryLocation nodes:
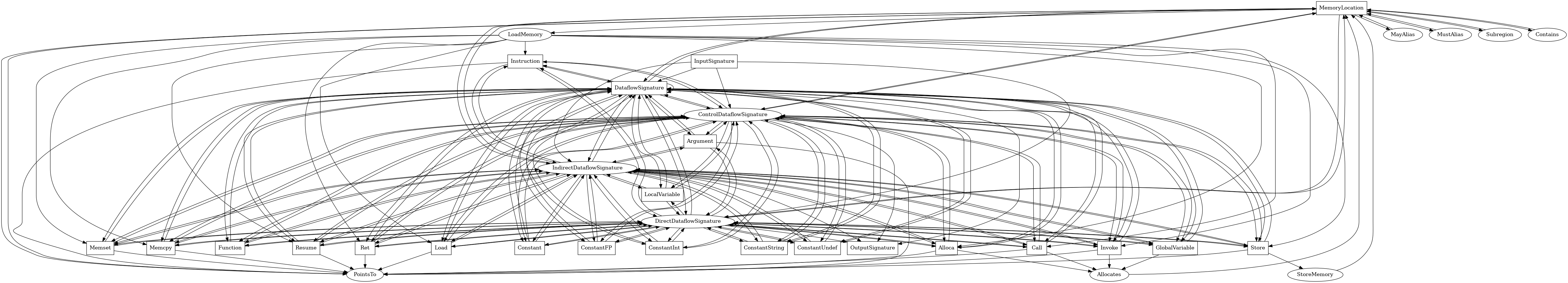
An abstract memory location represents a set of runtime heap locations.
Attributes:
node_kindpretty_stringtype:
string
alias_set_identifiertype:
string
allocation_contexttype:
string
allocation_size_bytes: The number of bytes allocated on the heap, as determined by the points-to analysis.type:
integer
DataflowSignature¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to DataflowSignature nodes:
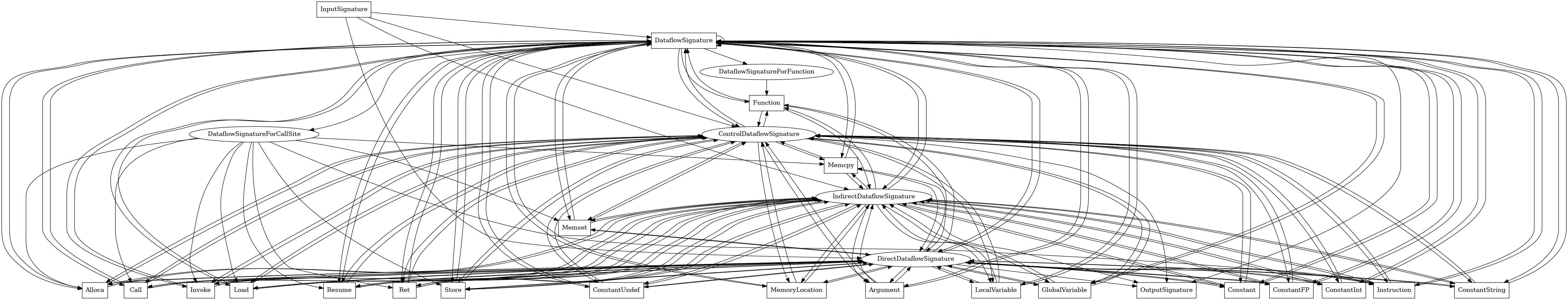
Abstract representation of a dataflow derived from a signature
Attributes:
node_kindtagstype:
array
contexttype:
string
deallocatortype:
string
InputSignature¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to InputSignature nodes:

Abstract representation of a dataflow input derived from a signature
Attributes:
node_kindtagstype:
array
contexttype:
string
OutputSignature¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to OutputSignature nodes:
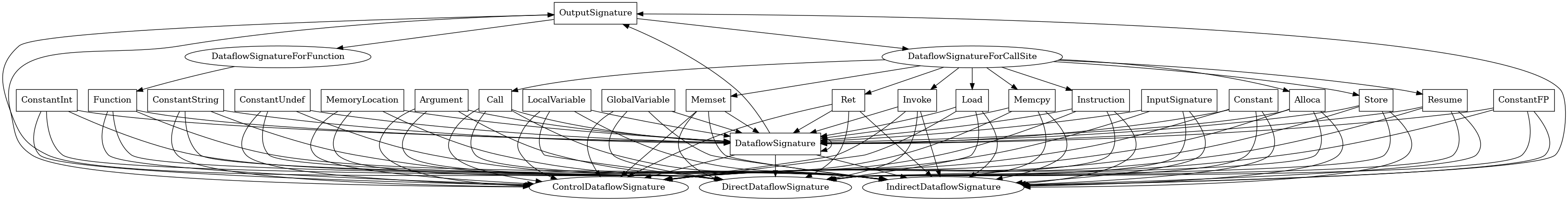
Abstract representation of a dataflow output derived from a signature
Attributes:
node_kindtagstype:
array
contexttype:
string
DWARFType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to DWARFType nodes:
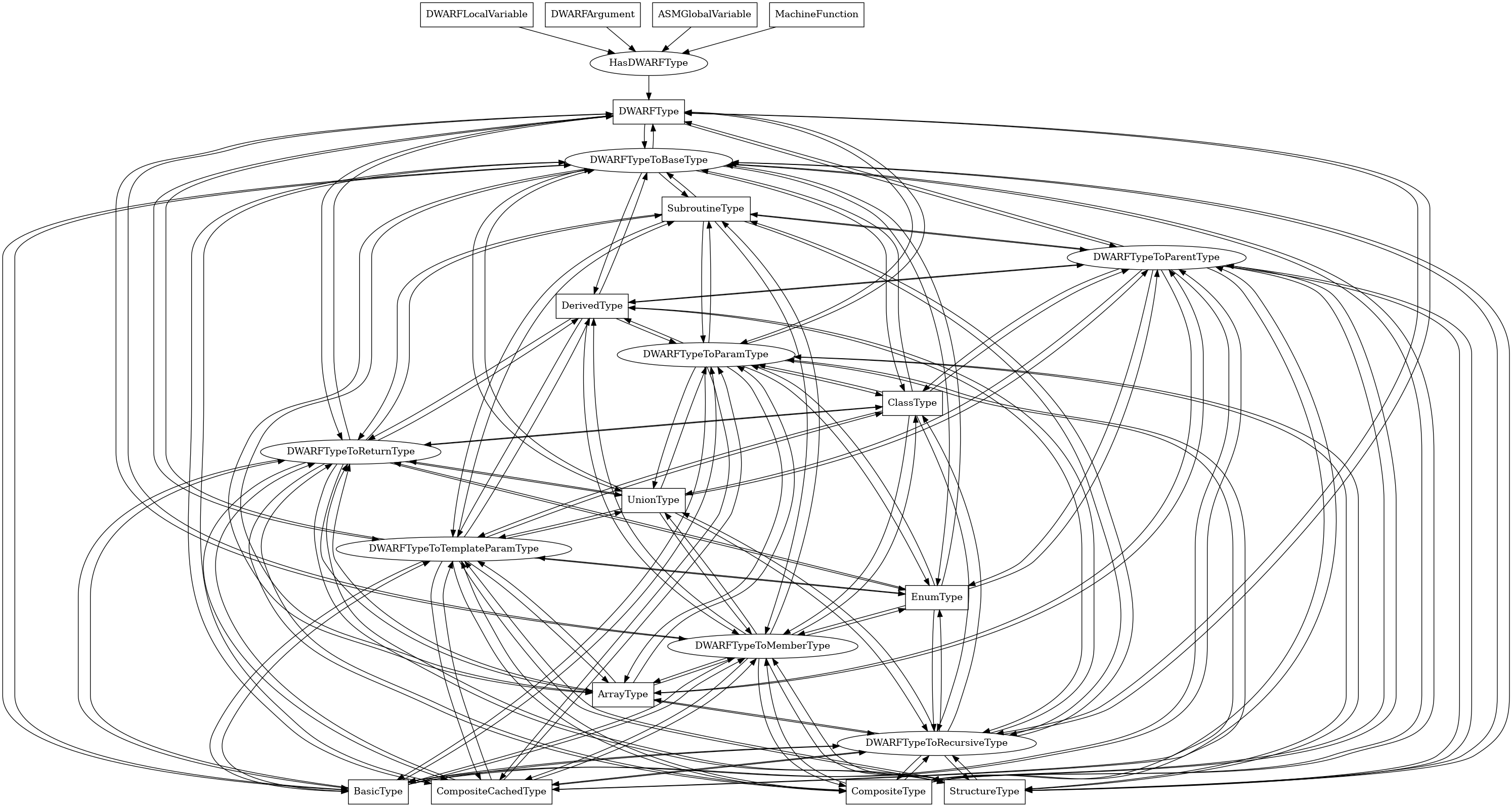
The DWARF representation of a type in the program
Attributes:
node_kind
BasicType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to BasicType nodes:
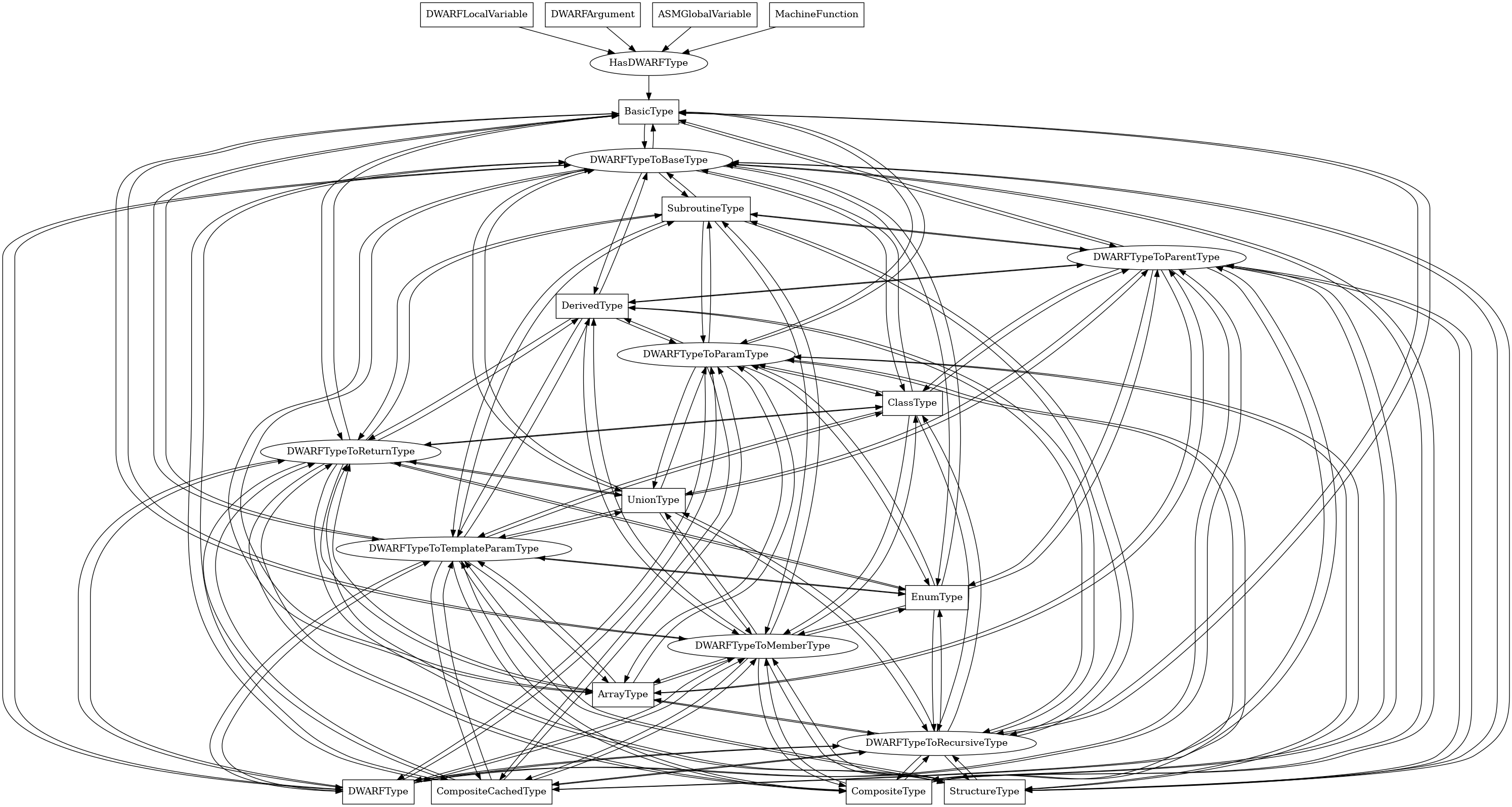
A basic DWARF type, corresponding to basic C or C++ types like int.
Attributes:
node_kind
CompositeType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to CompositeType nodes:
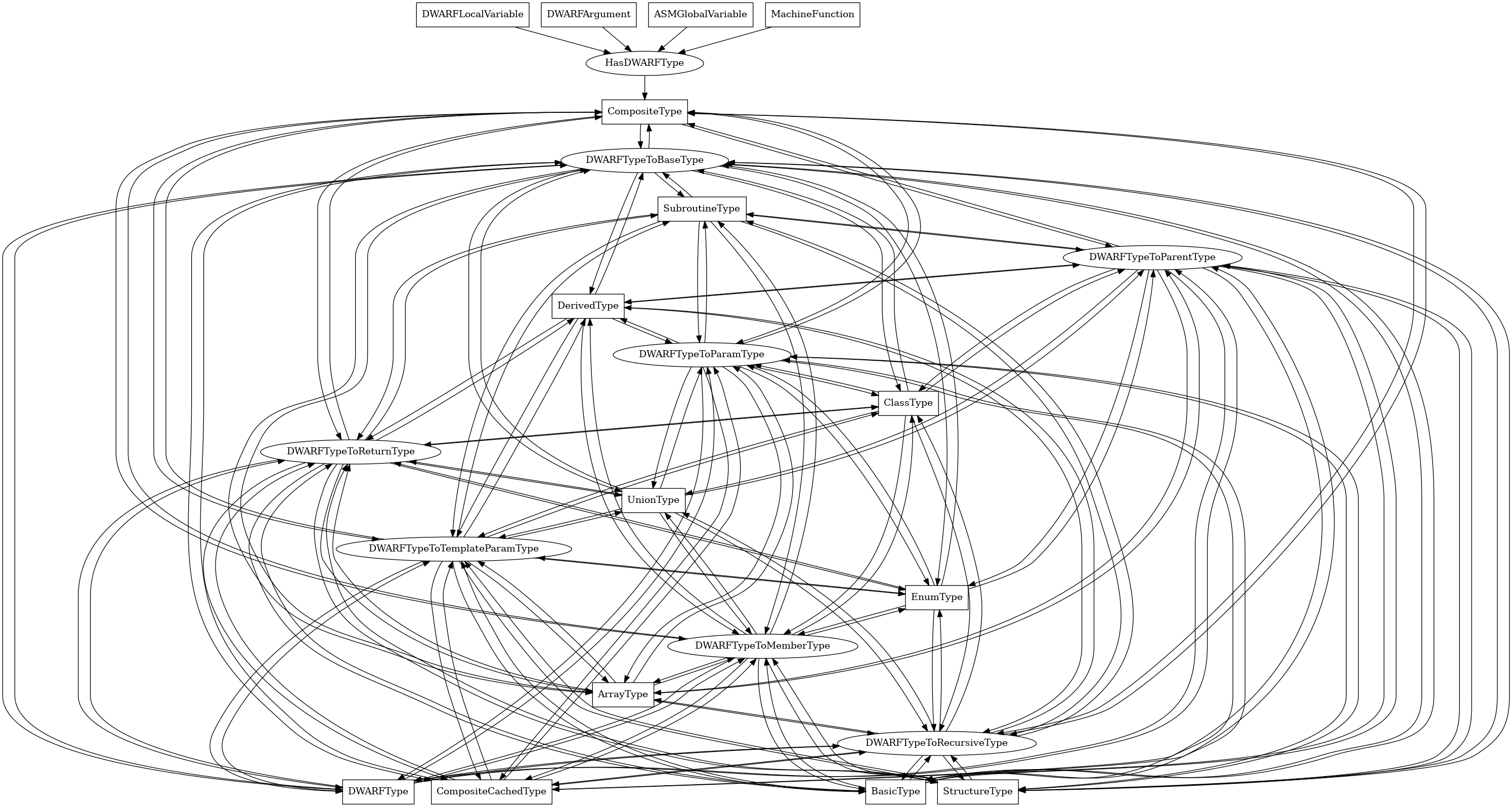
A composite DWARF type.
Attributes:
node_kind
CompositeCachedType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to CompositeCachedType nodes:
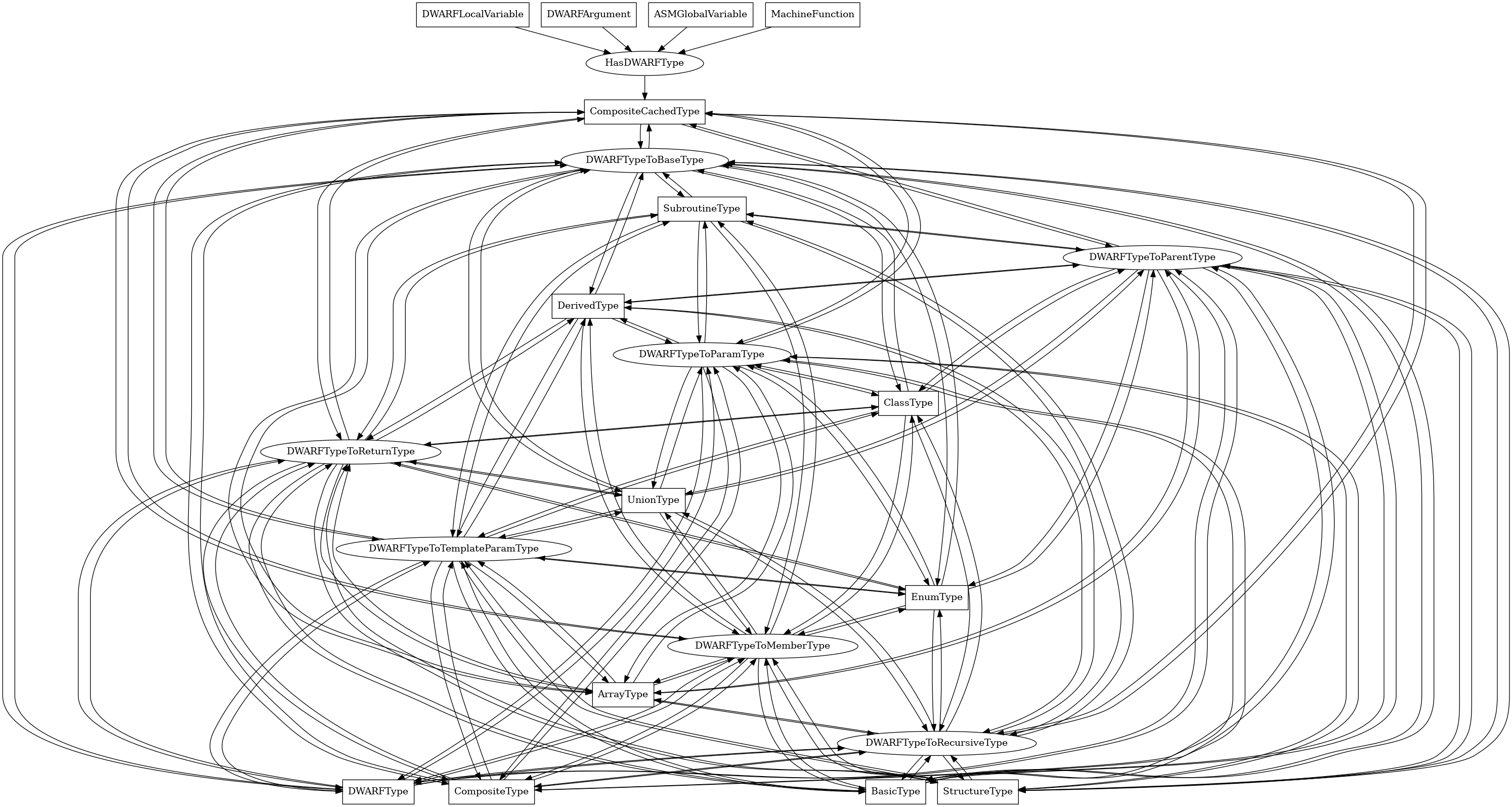
A composite cached DWARF type.
Attributes:
node_kind
StructureType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to StructureType nodes:
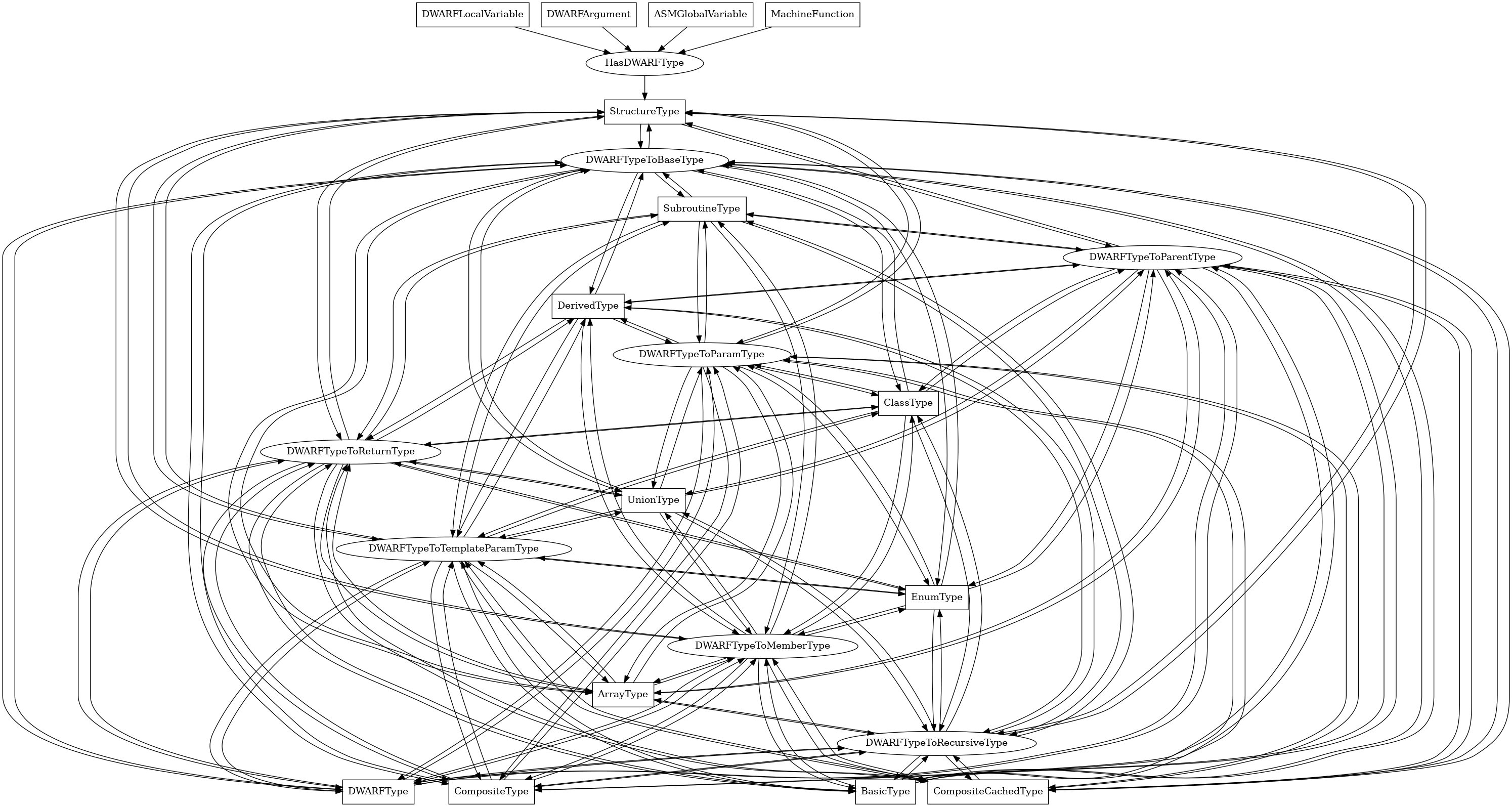
A DWARF struct type, corresponding to a C or C++ struct.
Attributes:
node_kind
ArrayType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ArrayType nodes:
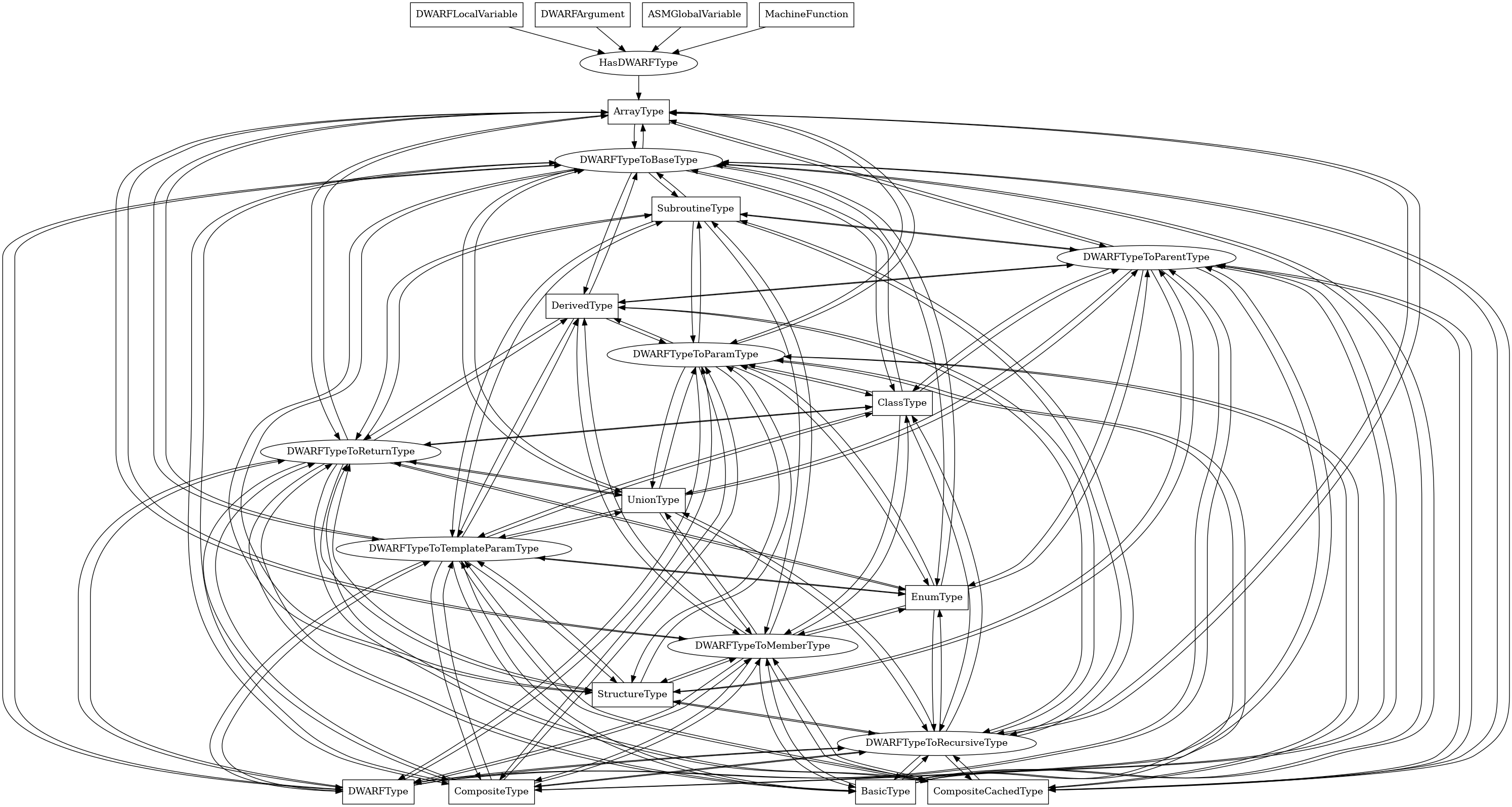
A DWARF array type, corresponding to a C or C++ array type.
Attributes:
node_kind
EnumType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to EnumType nodes:
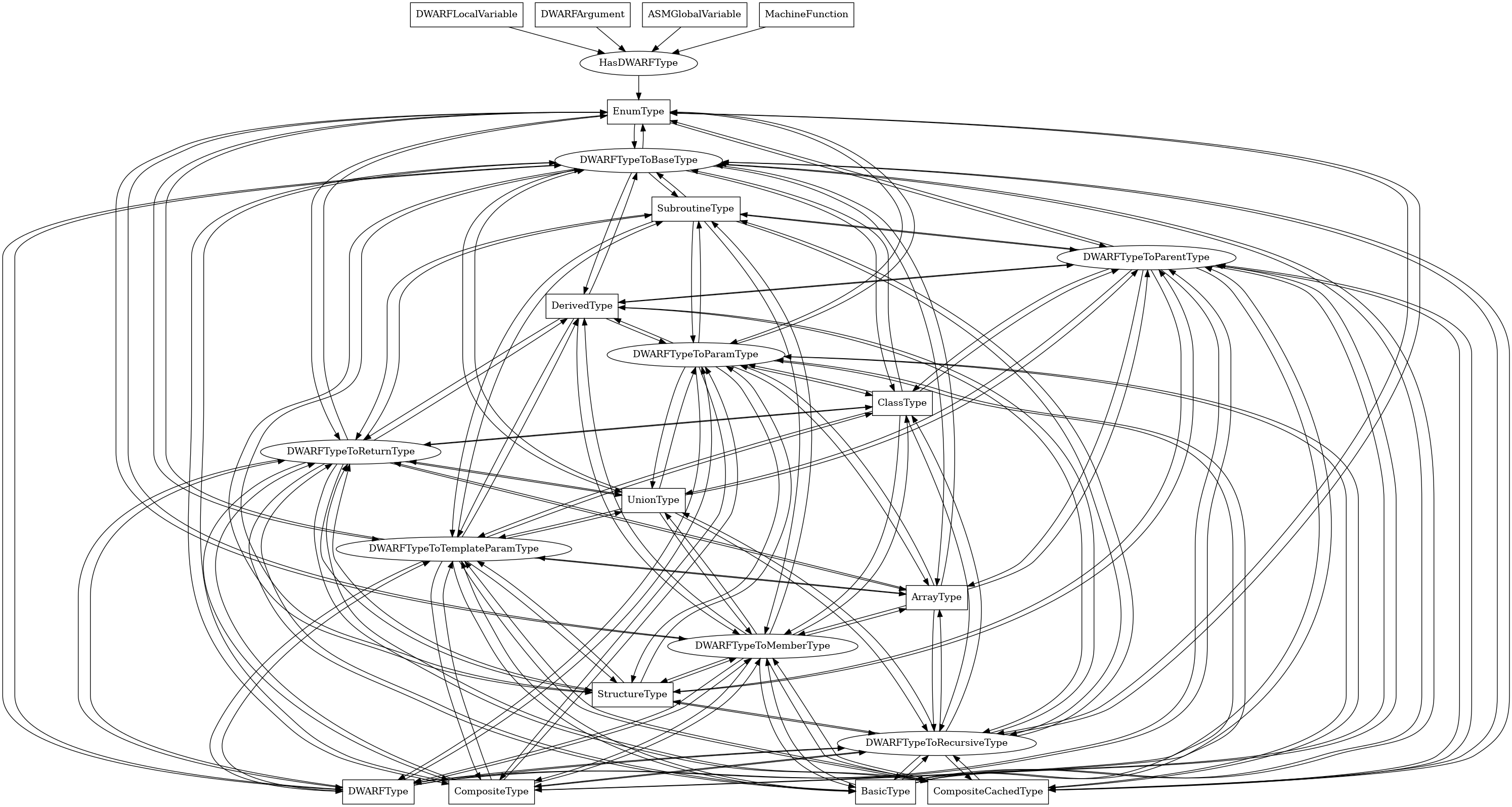
A DWARF enumeration type, corresponding to a C or C++ enum type.
Attributes:
node_kind
UnionType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to UnionType nodes:
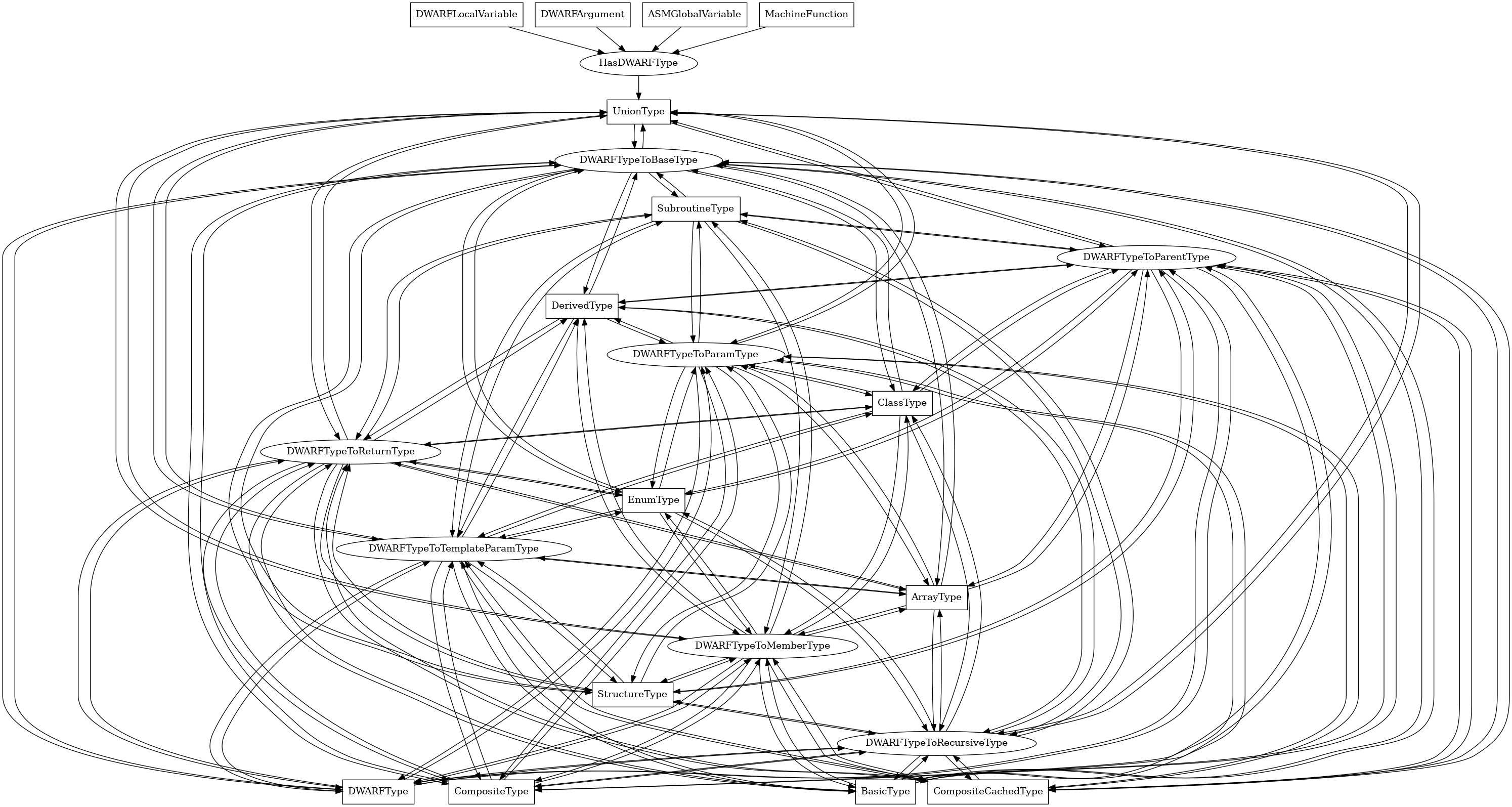
A DWARF union type, corresponding to a C or C++ union type.
Attributes:
node_kind
ClassType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to ClassType nodes:
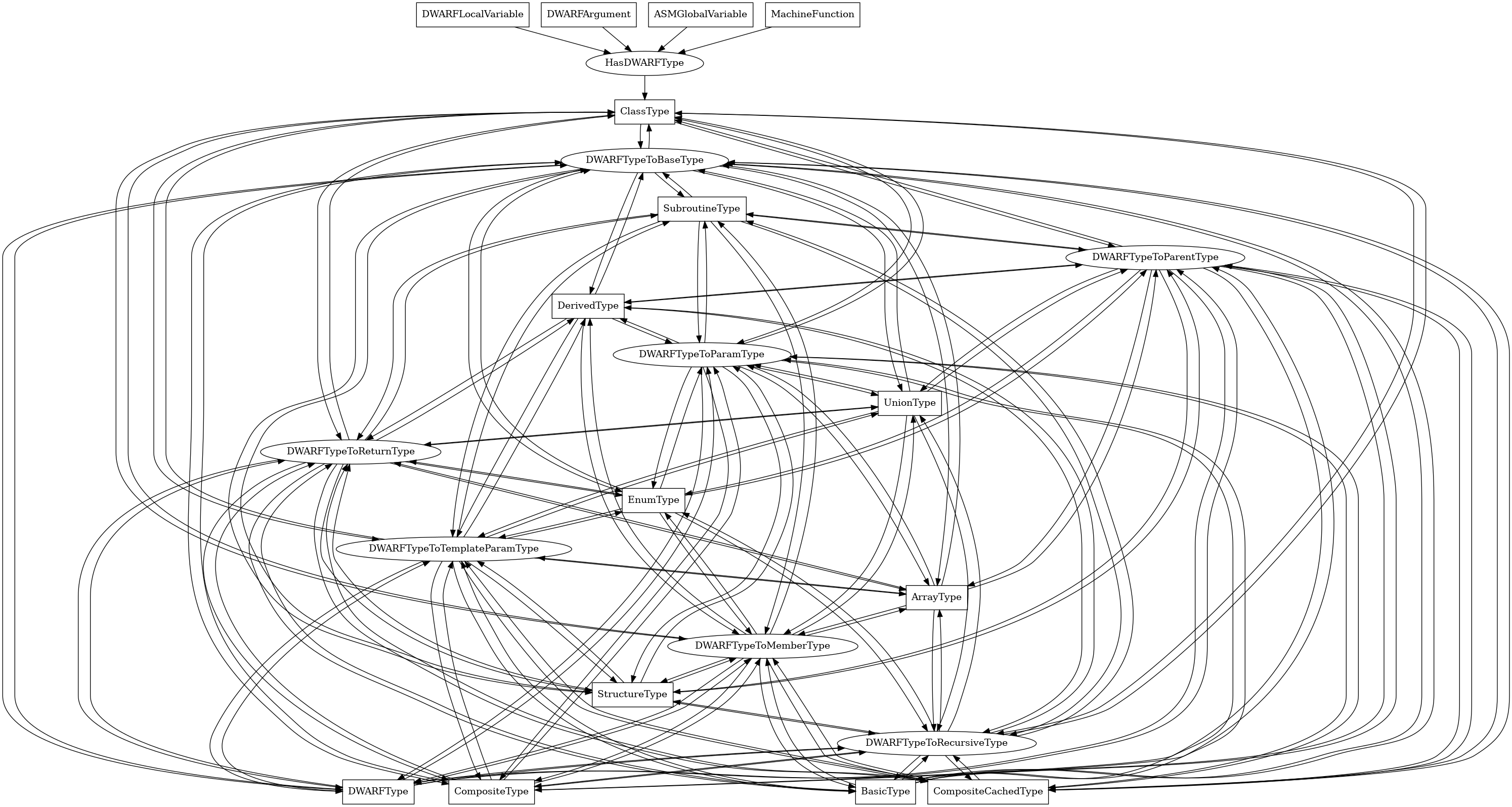
A DWARF class type, corresponding to a C++ class.
Attributes:
node_kind
DerivedType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to DerivedType nodes:
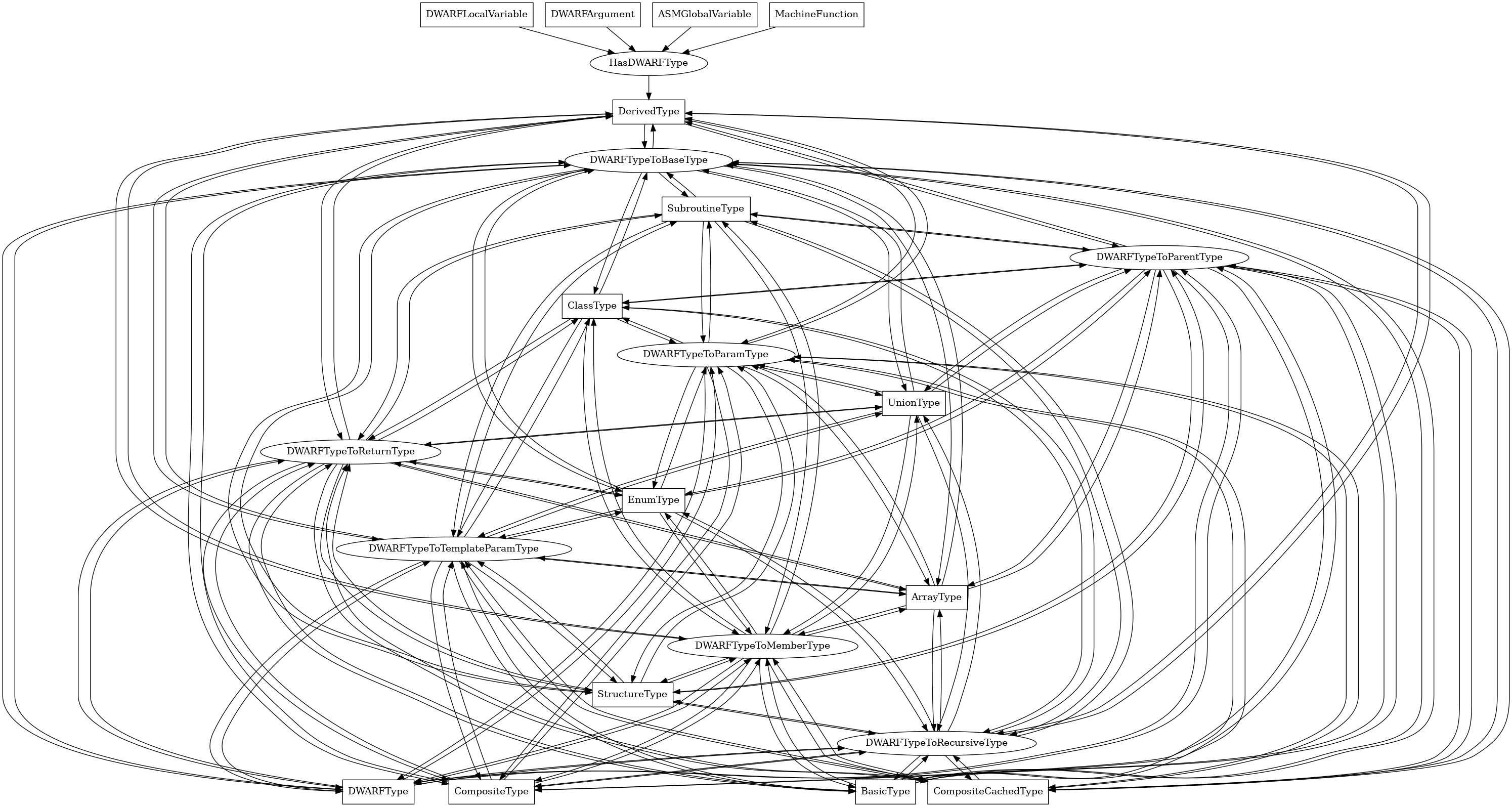
A DWARF derived type.
Attributes:
node_kind
SubroutineType¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to SubroutineType nodes:
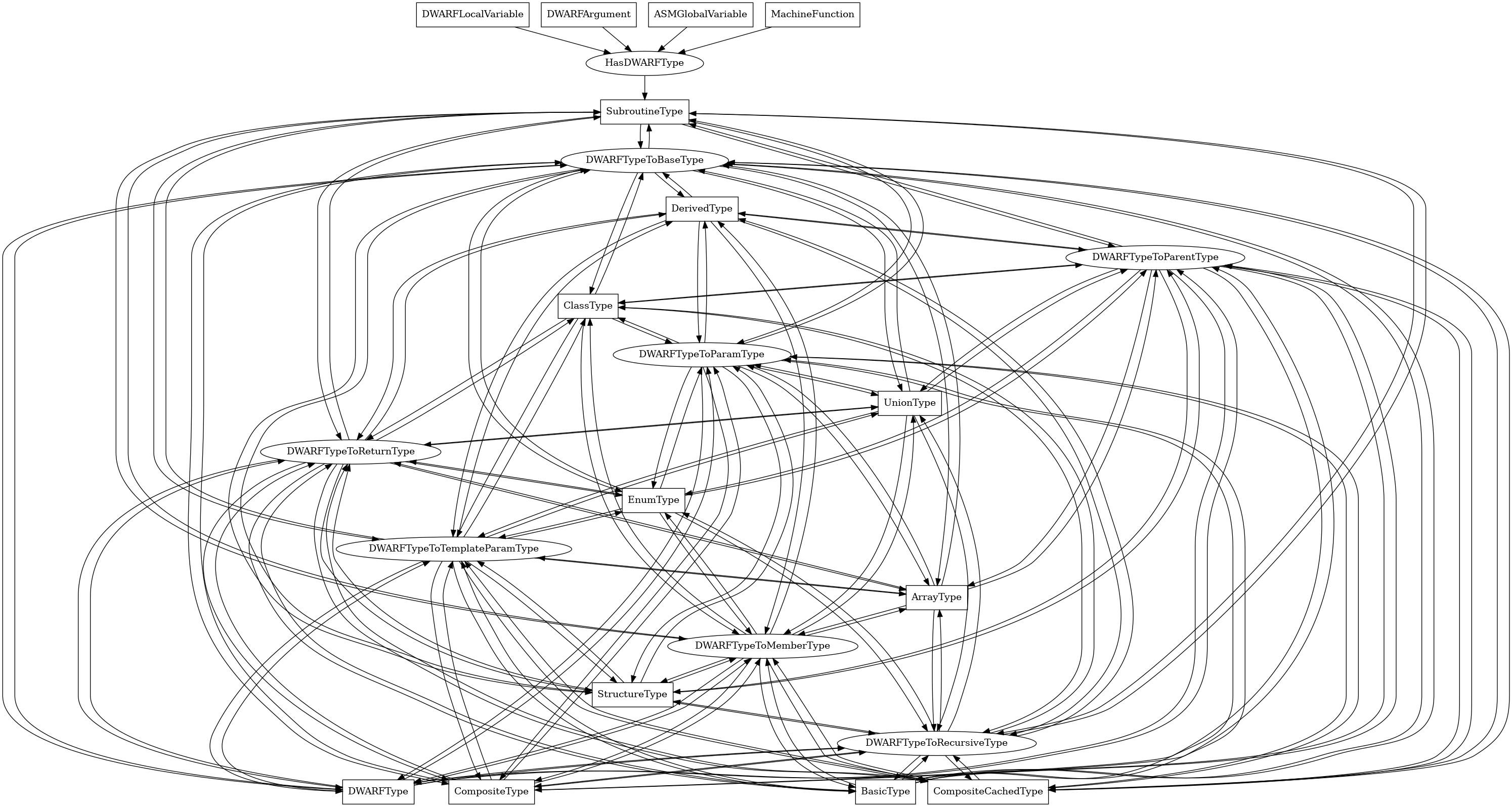
A DWARF subroutine type, corresponding to a C or C++ function or method type.
Attributes:
node_kind
Module¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to Module nodes:
The unified LLVM bitcode module that the program was compiled from
Attributes:
node_kindmodule_name: The name of the LLVM moduletype:
string
source_file: The source file that this module was loaded from, if from a single source filetype:
string
target_triple: The LLVM target tripletype:
string
data_layout: The LLVM datalayout stringtype:
string
symbols: A list of all symbols in the moduletype:
array
TranslationUnit¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to TranslationUnit nodes:
A translation unit in the compiled program
Attributes:
node_kindsource_language: The source language for this translation unit, as aDW_LANG_constanttype:
string
producer: An identifier for the compiler or tool that produced this translation unittype:
string
flags: The command line arguments that produced this translation unittype:
string
filename: The input/source filename for this translation unittype:
string
PLTStub¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to PLTStub nodes:
A stub for a function that’s accessed through the binary’s Procedure Linkage Table
Attributes:
node_kindsymbol: The linker symbol for this PLT entrytype:
string
va: The virtual address of this PLT entrytype:
integer
VTable¶
The following is an entity-relationship diagram which displays the portion of the CPG schema relevant to VTable nodes:
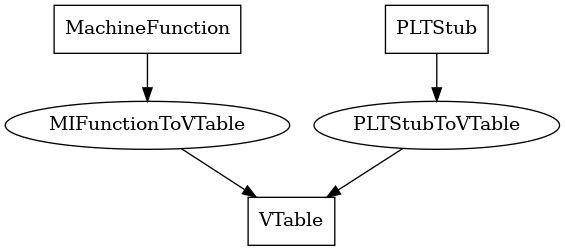
A virtual table for a C++ class
Attributes:
node_kindva: The virtual address for the virtual table itselftype:
integer
size: The size of the virtual table, in bytes. This includes the RTTI and ‘offset to base’ fieldstype:
integer
symbol: The linker symbol for this virtual tabletype:
string
class_name: The name of the C++ class that this virtual table belongs totype:
string
rtti_va: The virtual address to the RTTI entry for this virtual tabletype:
integer
members: The virtual addresses for each entry in the virtual tabletype:
array
Edges¶
FunctionToLocalVariable¶
These edges map LLVM-level functions to source-level local variables that the corresponding source-level function allocates.
Attributes:
edge_kind
FunctionToEntryBlock¶
Functions have a unique first basic block, which is always executed when that function is called.
Attributes:
edge_kind
BlockToSuccessorBlock¶
A block has a set of successor blocks, which is where control flow may transfer to from its terminator instruction.
Attributes:
edge_kind
InstructionToSuccessorInstruction¶
An instruction’s (control-flow) successors are the instructions that can execute immediately after it.
Attributes:
edge_kindcondition: Conditions appear on successor edges out of block terminator instructions such as ‘br’, which may transfer control to multiple targets.
HasLLVMType¶
Every LLVM ‘Value’ has a type, this edge captures that relationship.
Attributes:
edge_kind
Callgraph¶
This edge relates a function to functions it may call.
Attributes:
edge_kindcaller_contexttype:
string
callee_contexttype:
string
mod_ref_behavior: #/definitions/mod_ref_behavior
CallToFunction¶
This edge relates a ‘call’ or ‘invoke’ instruction to the function being called based on the pointer analysis.
Attributes:
edge_kindcaller_contexttype:
string
callee_contexttype:
string
mod_ref_behavior: #/definitions/mod_ref_behavior
MIFunctionToIRFunction¶
LLVM middle-end functions are paired with the corresponding LLVM IR function
Attributes:
edge_kind
MIFunctionToDWARFArgument¶
This edge relates a middle-end function to each of the formal parameters that occur in the function’s original source
Attributes:
edge_kind
MIFunctionToDWARFLocalVariable¶
This edge relates a middle-end function to each of the local variables that occur in the function’s original source
Attributes:
edge_kind
MIFunctionToVTable¶
This edge relates a middle-end function to its virtual table entries
Attributes:
edge_kind
MIBlockToIRBlock¶
LLVM middle-end basic blocks are paired with the corresponding LLVM IR basic block where possible
Attributes:
edge_kind
MIBlockToASMBlock¶
x86_64 basic blocks are paired with the corresponding LLVM middle-end basic block where possible
Attributes:
edge_kind
BlockToControlDependentBlock¶
Connects a basic block to all basic blocks whose execution may depend on the control-flow exiting the block.
Attributes:
edge_kindcondition: The value of the branch condition when leaving the terminating instruction of the block.controls: True if execution of the control dependent block is entirely dependent on the control-flow exiting the block.type:
boolean
TerminatorInstructionToControlDependentInstruction¶
Connects a branching instruction to all instructions whose execution depends on the control-flow exiting the instruction.
Attributes:
edge_kindcondition: The value of the branch condition when leaving the terminating instruction.controls: True if execution of the control instruction block is entirely dependent on the control-flow exiting the terminator instruction.type:
boolean
FunctionEntryToControlDependentBlock¶
Connects a function to all basic blocks whose execution depends solely on control-flow entering the function.
Attributes:
edge_kindconditioncontrols: True if execution of the control dependent block is entirely dependent on the control-flow entering the function.type:
boolean
FunctionEntryToControlDependentInstruction¶
Connects a function to all instructions whose execution depends solely on control-flow entering the function.
Attributes:
edge_kindconditioncontrols: True if execution of the control dependent instruction is entirely dependent on the control-flow entering the function.type:
boolean
ValueDefinitionToUse¶
This edge is similar to LLVM’s Use class, it connects a LLVM User with the LLVM Value it uses. This is a generic concept and applies in particular to e.g. an instruction ‘using’ its operands.
Attributes:
edge_kindoperand_numbertype:
integer
incoming_blocktype:
integer
is_callee: Is the value being used a function being called by thisinvokeorcallinstruction?type:
boolean
is_argument_operand: Is the value being used as an argument to the function being called by thisinvokeorcallinstruction?type:
boolean
CallToParamBinding¶
This edge connects a ‘call’ or ‘invoke’ instruction to all the relevant ‘ParamBinding’ nodes.
Attributes:
edge_kindcaller_contexttype:
string
callee_contexttype:
string
OperandToParamBinding¶
This edge connects a value used as an argument to an ‘Argument’ node, via a ‘ParamBinding’ node.
Attributes:
edge_kindcaller_contexttype:
string
callee_contexttype:
string
ParamBindingToArg¶
This edge connects a value used as an argument to an ‘Argument’ node, via a ‘ParamBinding’ node.
Attributes:
edge_kindcaller_contexttype:
string
callee_contexttype:
string
SameCall¶
This edge connects a ‘ParamBinding’ node with a ‘CallReturn’ node that corresponds to the same call site.
Attributes:
edge_kind
ReturnValueToCallReturn¶
This edge connects a value used in a return instruction to the corresponding callsite, via a ‘CallReturn’ node.
Attributes:
edge_kindcaller_contexttype:
string
callee_contexttype:
string
ReturnInstructionToCallReturn¶
This edge connects a return instruction to the corresponding callsite, via a ‘CallReturn’ node.
Attributes:
edge_kindcaller_contexttype:
string
callee_contexttype:
string
CallReturnToCaller¶
This edge connects a value used in a return statement to the corresponding callsite, via a ‘CallReturn’ node.
Attributes:
edge_kindcaller_contexttype:
string
callee_contexttype:
string
PointsTo¶
Connects a node representing a pointer to memory locations it might refer to.
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
MayAlias¶
This edge connects two abstract memory locations that could represent the same field or array index if they abstract the same concrete memory object. For example, ‘buf[*]’ and ‘buf[0]’.
Attributes:
edge_kind
MustAlias¶
This edge connects two abstract memory locations that must represent the same field or array index if they abstract the same concrete memory object.
Attributes:
edge_kind
Subregion¶
This edge connects an abstract memory location to memory locations that are its immediate subobjects. For example, ‘buf[1]’ is a subobject of ‘buf’.
Attributes:
edge_kind
Contains¶
This edge connects an abstract memory location to memory locations that it contains, recursively. For example, ‘buf[1]’ is a subobject of ‘buf’.
Attributes:
edge_kind
StoreMemory¶
Connects an instruction to memory locations it may store to.
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
LoadMemory¶
Connects an instruction to memory locations it may load from.
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
Allocates¶
This edge connects an ‘alloca’ instruction or call to ‘malloc’ with an abstract memory location.
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
HasDWARFType¶
This edge connects variables (and function arguments) to their DWARF type information
Attributes:
edge_kind
DWARFTypeToBaseType¶
This edge connects a DWARF derived type to its “base” type (or a “base” type to its deriving type(s))
Attributes:
edge_kind
DWARFTypeToRecursiveType¶
This edge connects a recursive DWARF type to its initial type definition
Attributes:
edge_kind
DWARFTypeToMemberType¶
This edge connects a DWARF type to its constituent member types (fields, union variants, etc.)
Attributes:
edge_kind
DWARFTypeToTemplateParamType¶
This edge connects a DWARF type to its constituent template parameter types
Attributes:
edge_kind
DWARFTypeToReturnType¶
This edge connects a DWARF type to its constituent function return type
Attributes:
edge_kind
DWARFTypeToParamType¶
This edge connects a DWARF type to its constituent function parameter types
Attributes:
edge_kind
DWARFTypeToParentType¶
This edge connects a DWARF type to the parent class or structure that it inherits from
Attributes:
edge_kind
GlobalToInitializer¶
This edge connects global variables to their (constant) initializers
Attributes:
edge_kind
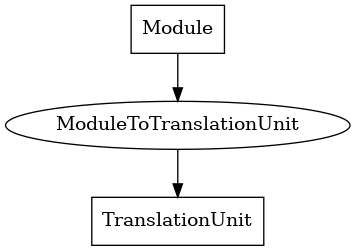
ModuleToTranslationUnit¶
This edge connects the main LLVM module to each of its constituent translation units
Attributes:
edge_kind
LocalVariableToDWARFLocalVariable¶
This edge connects an LLVM-level local variable to its DWARF counterpart
Attributes:
edge_kind
ArgumentToDWARFArgument¶
This edge connects an LLVM-level function argument to its DWARF counterpart
Attributes:
edge_kind
DataflowSignature¶
This edge represents dataflows that are external to the program and included via signatures
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
DirectDataflowSignature¶
This edge represents dataflows that are external to the program and included via signatures; this is a direct flow, meaning the target value is computed from the source value.
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
IndirectDataflowSignature¶
This edge represents dataflows that are external to the program and included via signatures; this is an indirect flow, meaning the target’s value changes depending on the source value, but it is not computed from the source value.
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
ControlDataflowSignature¶
This edge represents dataflows that are external to the program and included via signatures; this is a control flow, meaning the source value effects whether the target value is computed.
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
DataflowSignatureForCallSite¶
This edge connects a dataflow signature with the callsite it models
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
DataflowSignatureForFunction¶
This edge connects a dataflow signature with the function it models
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
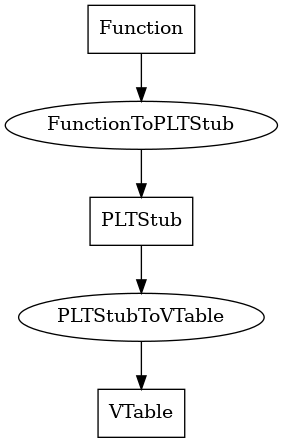
FunctionToPLTStub¶
This edge connects an LLVM-level function to its PLT stub in the compiled program, if it has one
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
PLTStubToVTable¶
This edge connects a PLT stub to the virtual tables that it’s present in, if any
Attributes:
edge_kindcontexttype:
string
Definitions¶
#/definitions/dwarf_type_kind¶
#/definitions/constant¶
#/definitions/instruction¶
#/definitions/location¶
A location in a source-language file
type:
objectattributes:
file: A location in a source-language file
type:
string
dir: A location in a source-language file
type:
string
column: A location in a source-language file
type:
integer
line: A location in a source-language file
type:
integer
function: A location in a source-language file
type:
string
compressed_id: A location in a source-language file
type:
string
#/definitions/definition_location¶
A definition location for a global variable in a source-language file
type:
objectattributes:
directory: A definition location for a global variable in a source-language file
type:
string
filename: A definition location for a global variable in a source-language file
type:
string
line: A definition location for a global variable in a source-language file
type:
integer
#/definitions/dwarf_location¶
Location of this variable in memory, expressed as either an absolute address or an offset from a register
type:
arrayattributes:
#/definitions/dwarf_type_common_info¶
A subobject common to every variant of dwarf_type
type:
objectattributes:
name: The name of the type, or empty if inapplicable
type:
string
tag: The DWARF tag (DW_TAG_*) for the type
type:
string
size: The size of the type, in bytes
type:
integer
align: The alignment of the type, in bytes
type:
integer
offset: The offset of this type within its parent, if applicable
type:
integer
forward_decl: Whether or not this type is forward-declared
type:
boolean
virtual: Whether or not this type is virtual
type:
boolean
artificial: Whether or not this type is artificial (i.e., not present in source)
type:
boolean
#/definitions/dwarf_template_param_value¶
A value in a C++ template value parameter
type:
objectattributes:
#/definitions/dwarf_type¶
A structured representation of C types, using DWARF identifiers.
type:
objectattributes:
#/definitions/source_scope¶
Source scoping information using DWARF
type:
objectattributes:
filename: The basename of the source file that this scope appears in
type:
string
directory: The directory of the source file that this scope appears in
type:
string
name: The scope’s name, if named
type:
string
linkage_name: The scope’s linkage name, if available and named
type:
string
tag: The DWARF tag corresponding to the scope kind
type:
string
parent_scope: Source scoping information using DWARF: #/definitions/source_scope
type:
object
#/definitions/dwarf_scope¶
A representation of the nearest enclosing lexical scope. The enclosing scope will also contain VA range information, unless it has been optimized away.
type:
objectattributes:
tag: The DWARF tag for this scope
type:
string
line: The source line that the scope starts on
type:
integer
contiguous: Whether the scope is laid out continuously in the binary
type:
boolean
inlined: Whether the scope has been inlined
type:
boolean
va_start: The start virtual address for the scope, if contiguous and not inlined
type:
integer
va_end: The end virtual address for the scope, if contiguous and not inlined
type:
integer
range_list: A list of virtual address ranges, if the scope is non-contiguous and not inlined
type:
array
#/definitions/source_location¶
The source location for a program feature
type:
objectattributes:
line: The source line
type:
integer
column: The source column
type:
integer
probably_optimized_away: Whether this location was probably optimized away
type:
boolean
llvm_func_name: The LLVM-level name of the function that this location is in
type:
string
func_name: The binary-level name of the function that this location is in
type:
string
bb_operand: The LLVM-level basic block operand that this location is in
type:
string
#/definitions/llvm_type¶
A structured representation of types in the LLVM type system. See https://llvm.org/docs/LangRef.html#type-system.
attributes:
#/definitions/value¶
Generally an instance of LLVM’s ‘Value’ class, these have associated unstructured, human-readable string representations
type:
objectattributes:
pretty_string: Generally an instance of LLVM’s ‘Value’ class, these have associated unstructured, human-readable string representations
type:
string
#/definitions/symbol¶
A symbol in the compiled program’s symbol table (.symtab)
type:
objectattributes:
name: The symbol’s name
type:
string
va: The symbol’s target address
type:
integer
size: The size, in bytes, of the entity represented by this symbol
type:
integer
binding: The symbol’s binding
type:
string
type: The symbol’s type
type:
string
visibility: The symbol’s visibility
type:
string